Anatomy And Injuries Of The Shoulder
Normal Shoulder Anatomy (Anterior View)
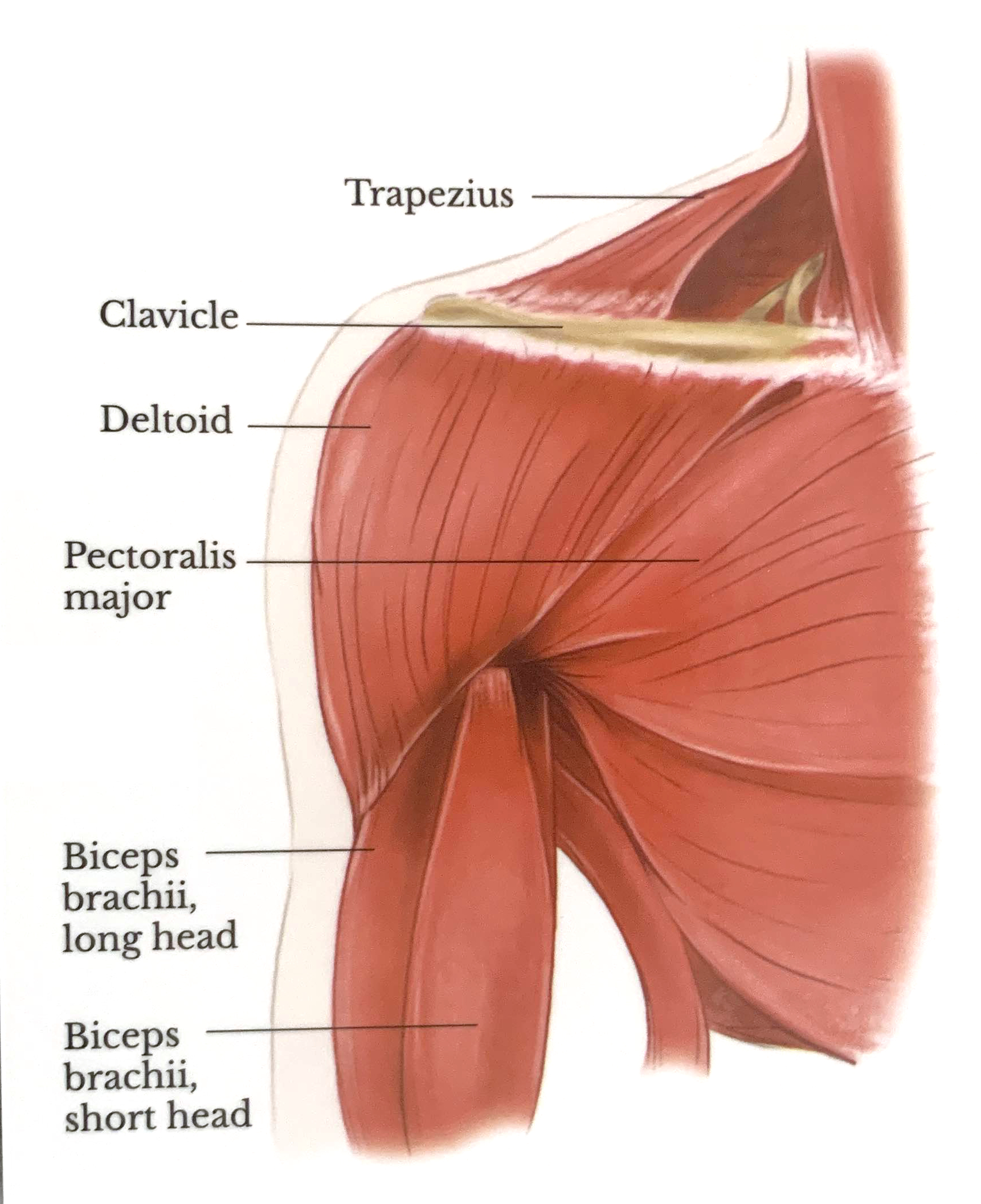
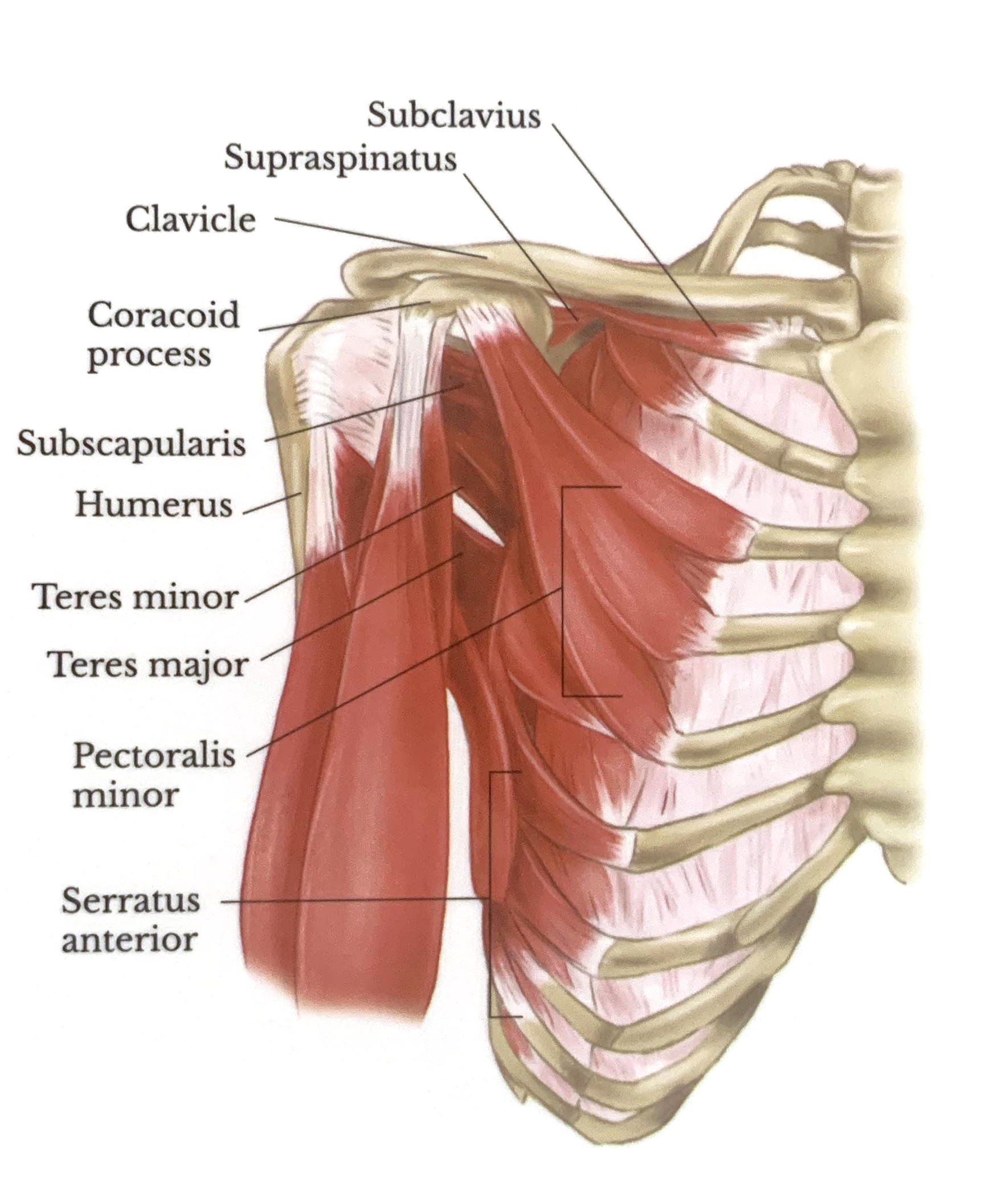
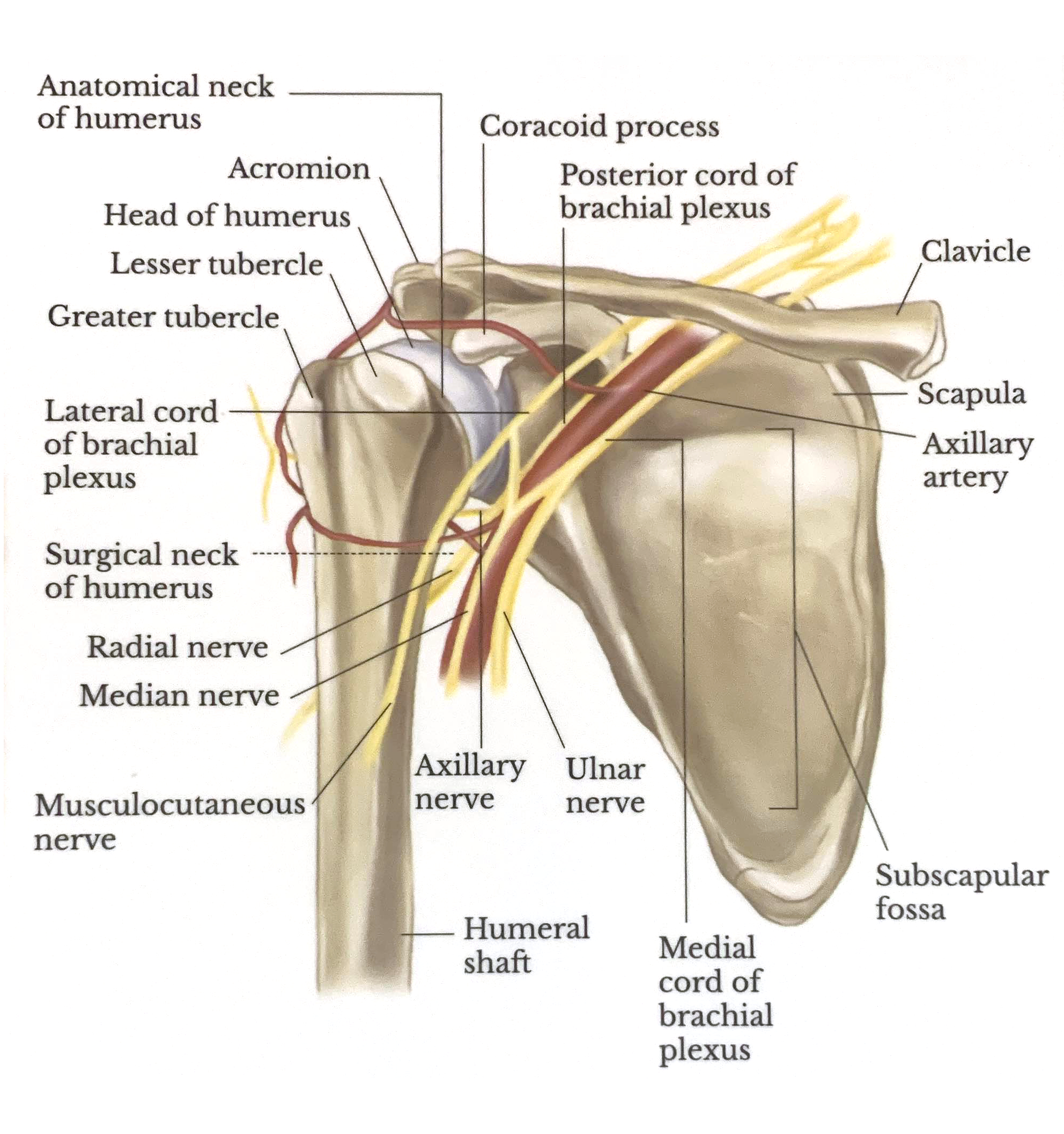
Lateral View
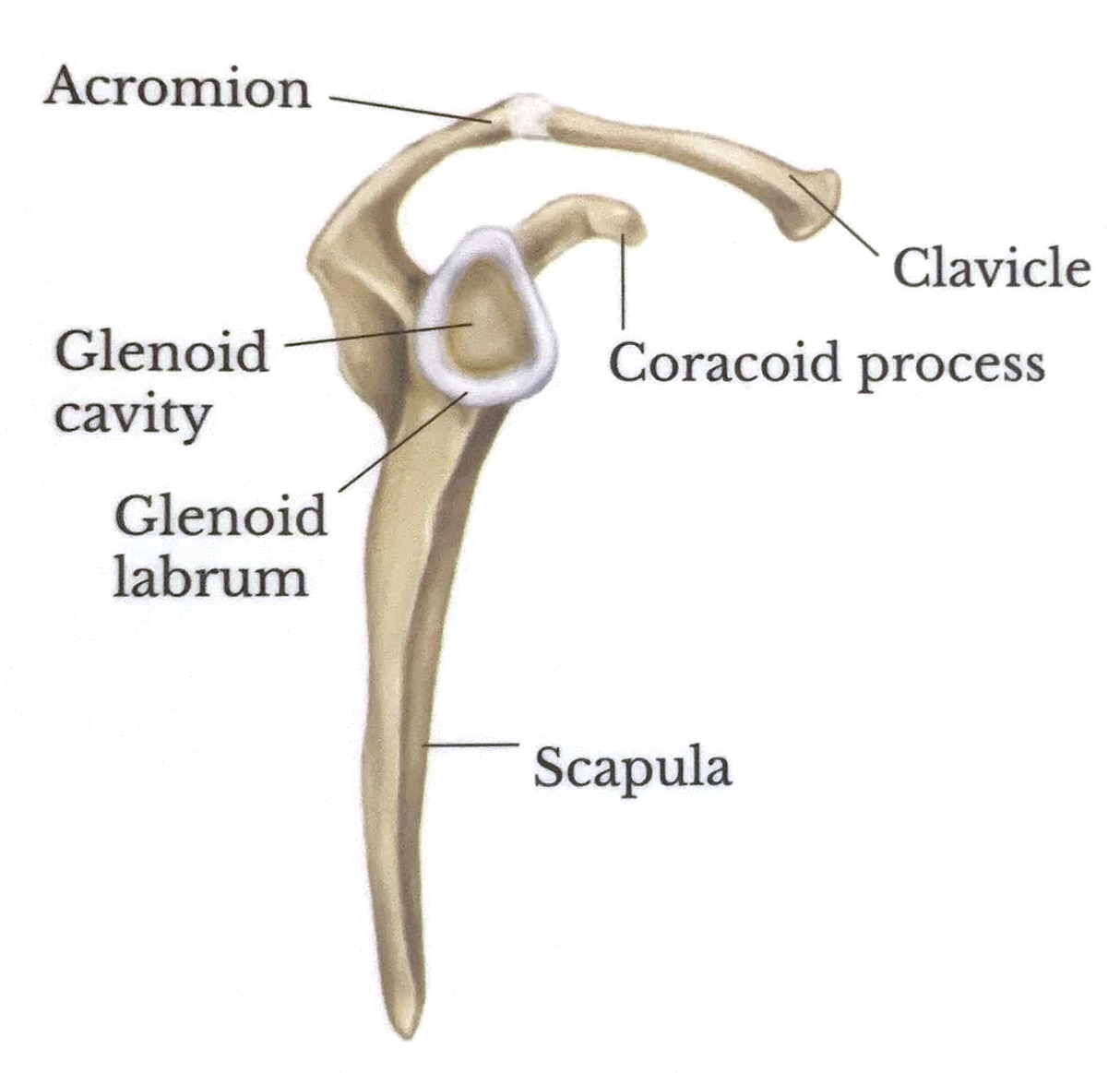
Lateral View With Joint Opened
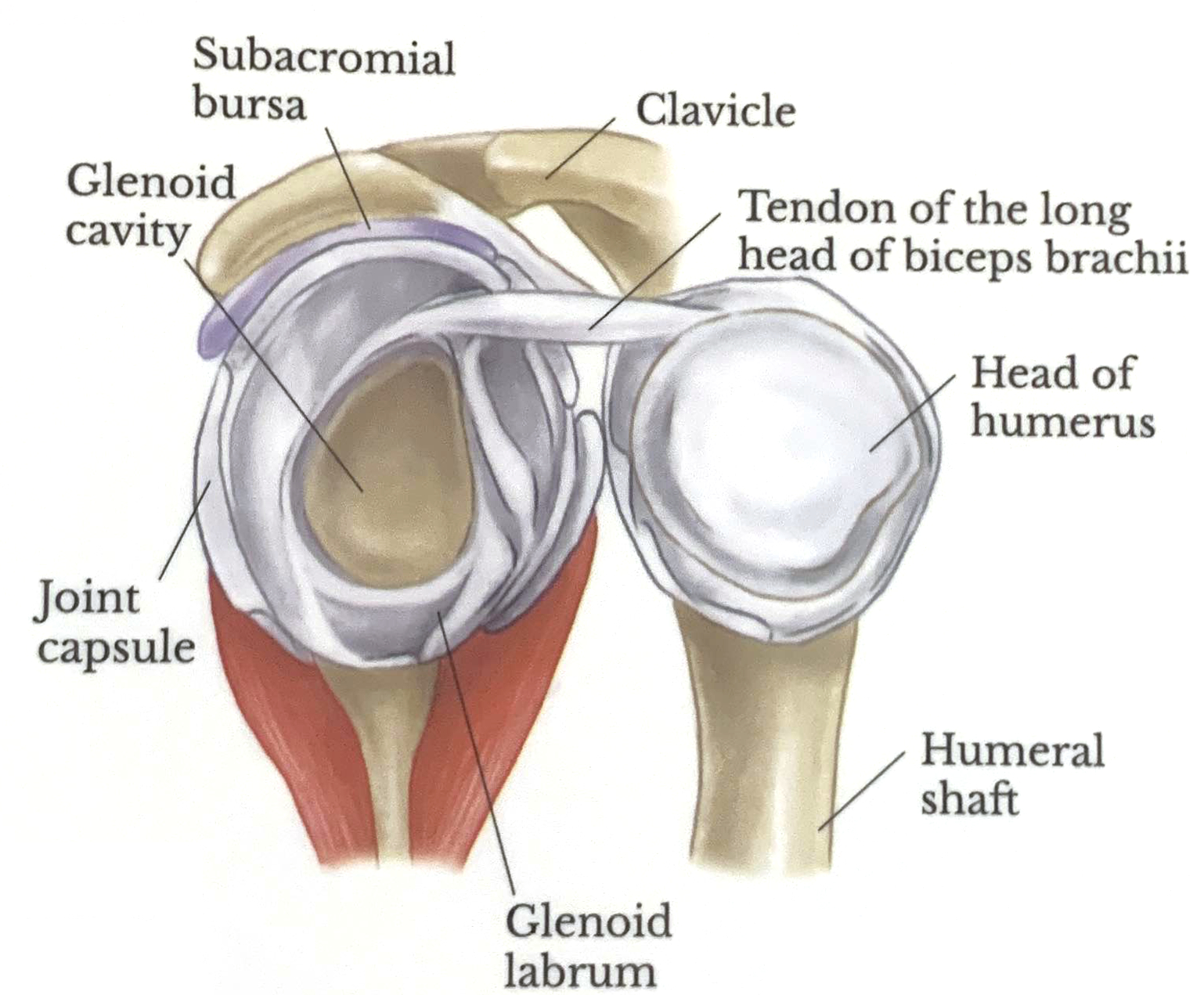
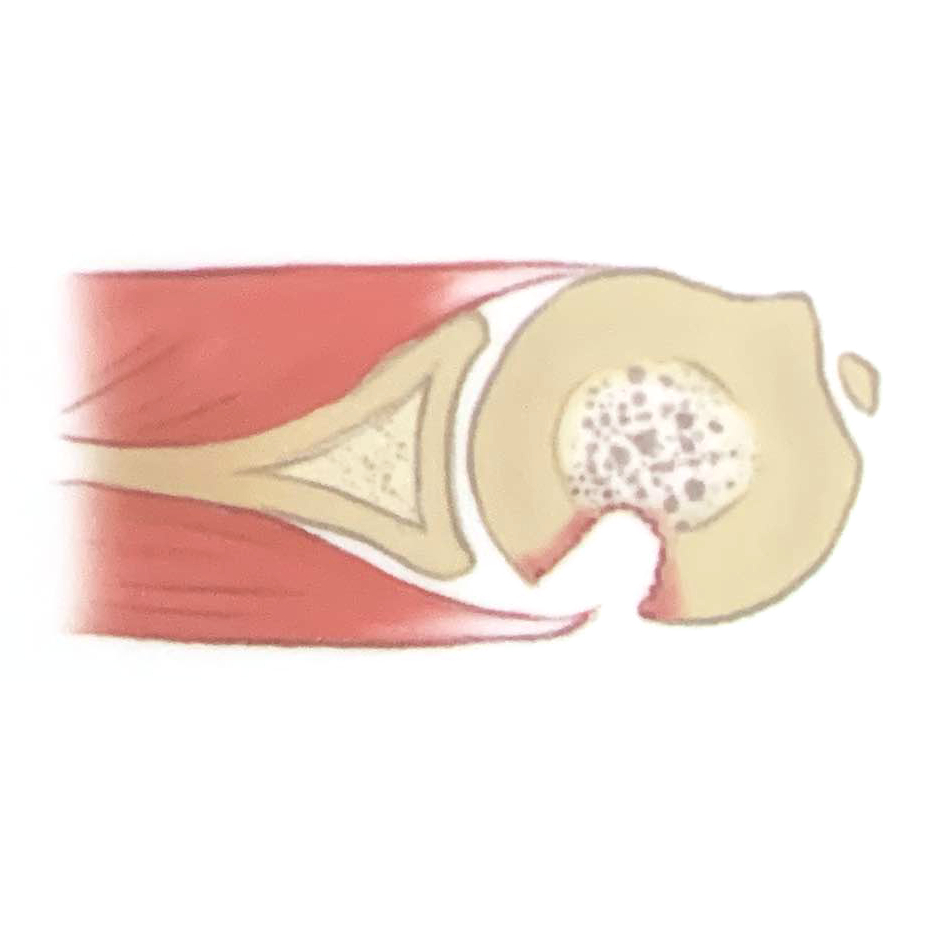
Proximal Humerus Fractures
All of these fractures can lead to neurovascular complications, usually involving the axillary nerve, suprascapular nerve, and axillary artery. The surgical neck fracture is the most common fracture of the proximal humerus.
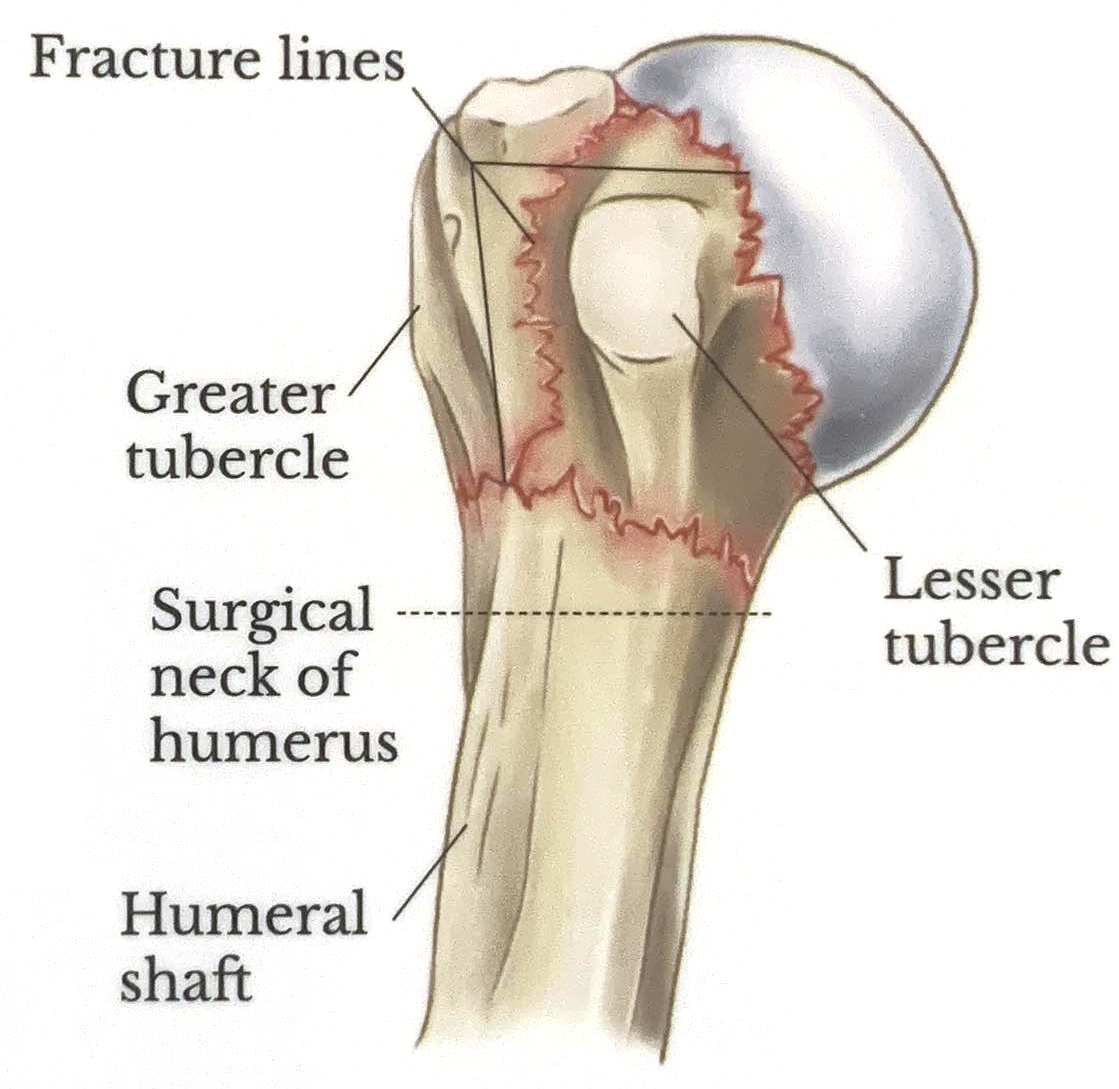
Rotator Cuff
The rotator cuff consists of the surpaspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis (SITS). These muscles are responsible for stabilizing the glenohumeral joint and contribute to the proper motion of the upper limbs.
Normal Position
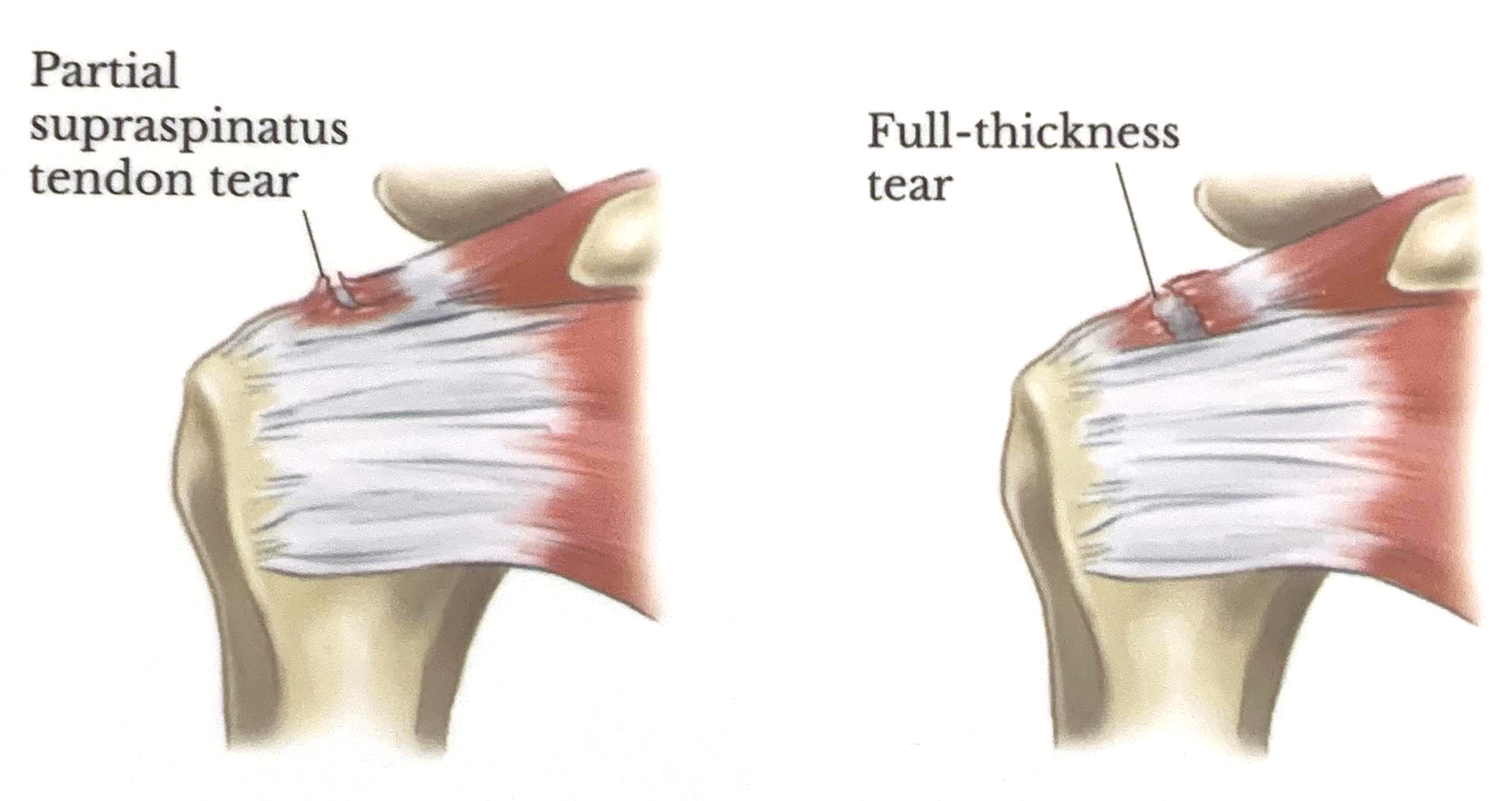
Rotator Cuff Tear
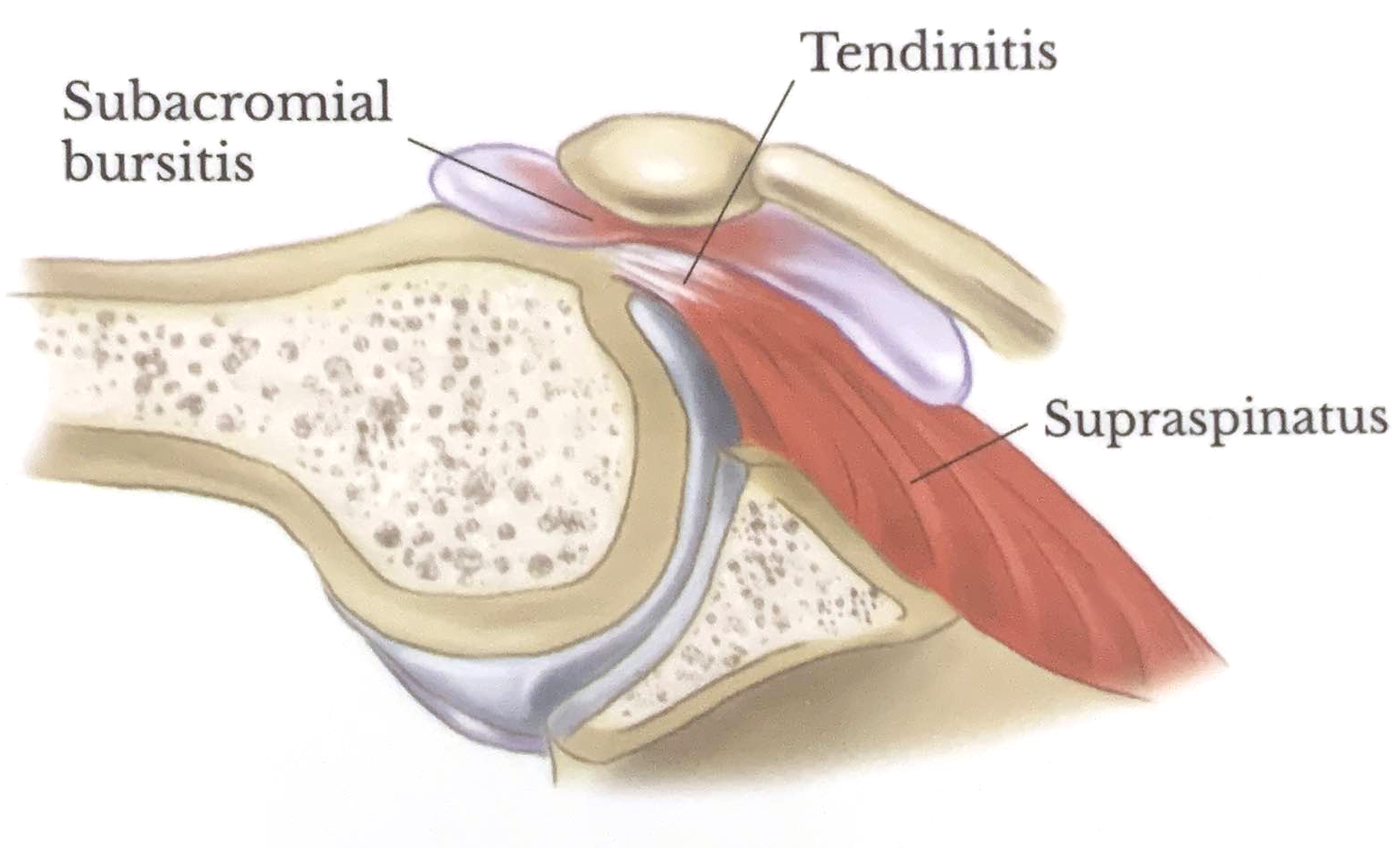
Impingement Syndrome
Shoulder impingement syndrome (painful arc syndrome, swimmer's shoulder, thrower's shoulder) occurs when the subacromial bursa and supraspinatus tendon become entrapped between the acromion and surrounding bony structures.
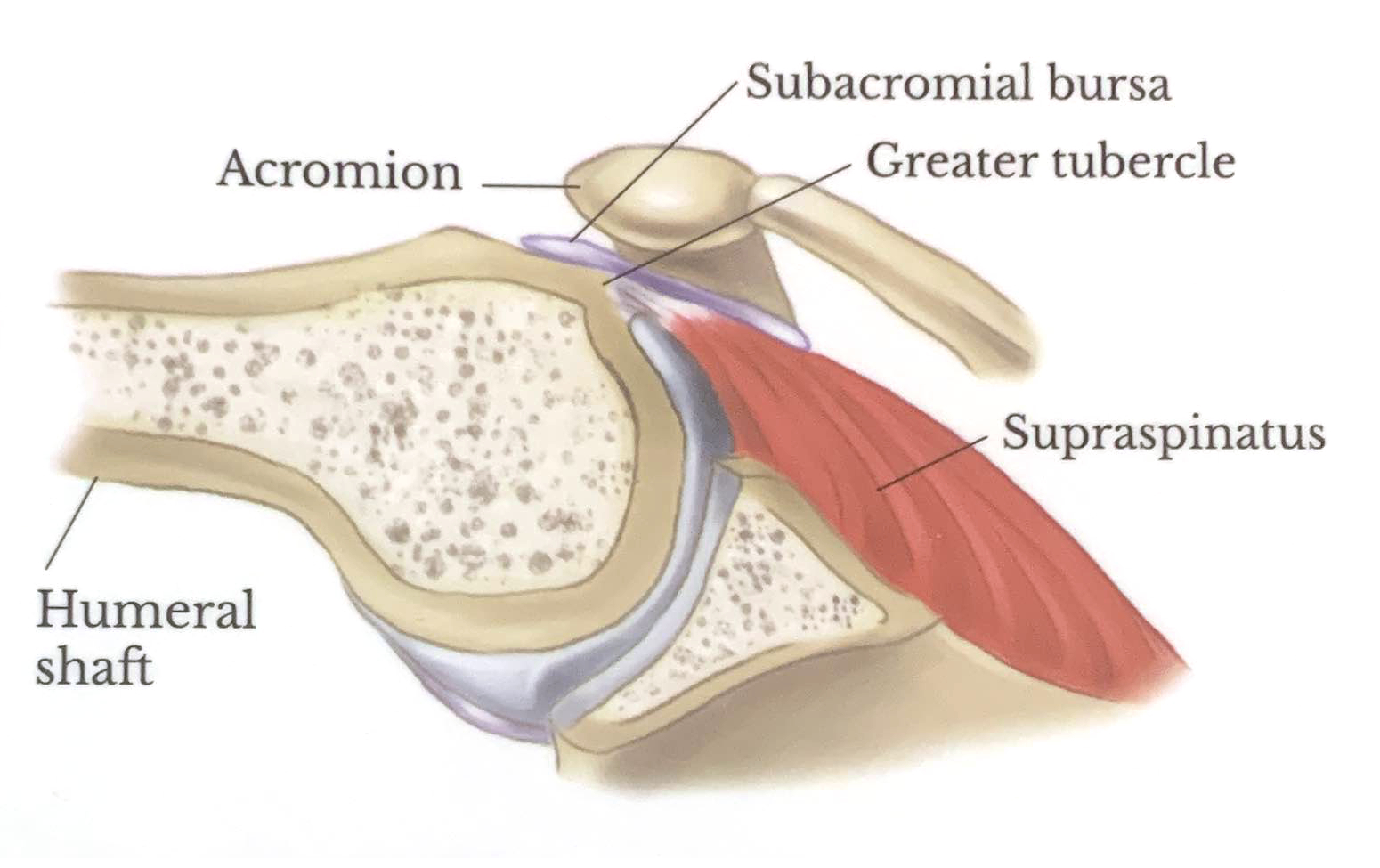
Normal Joint
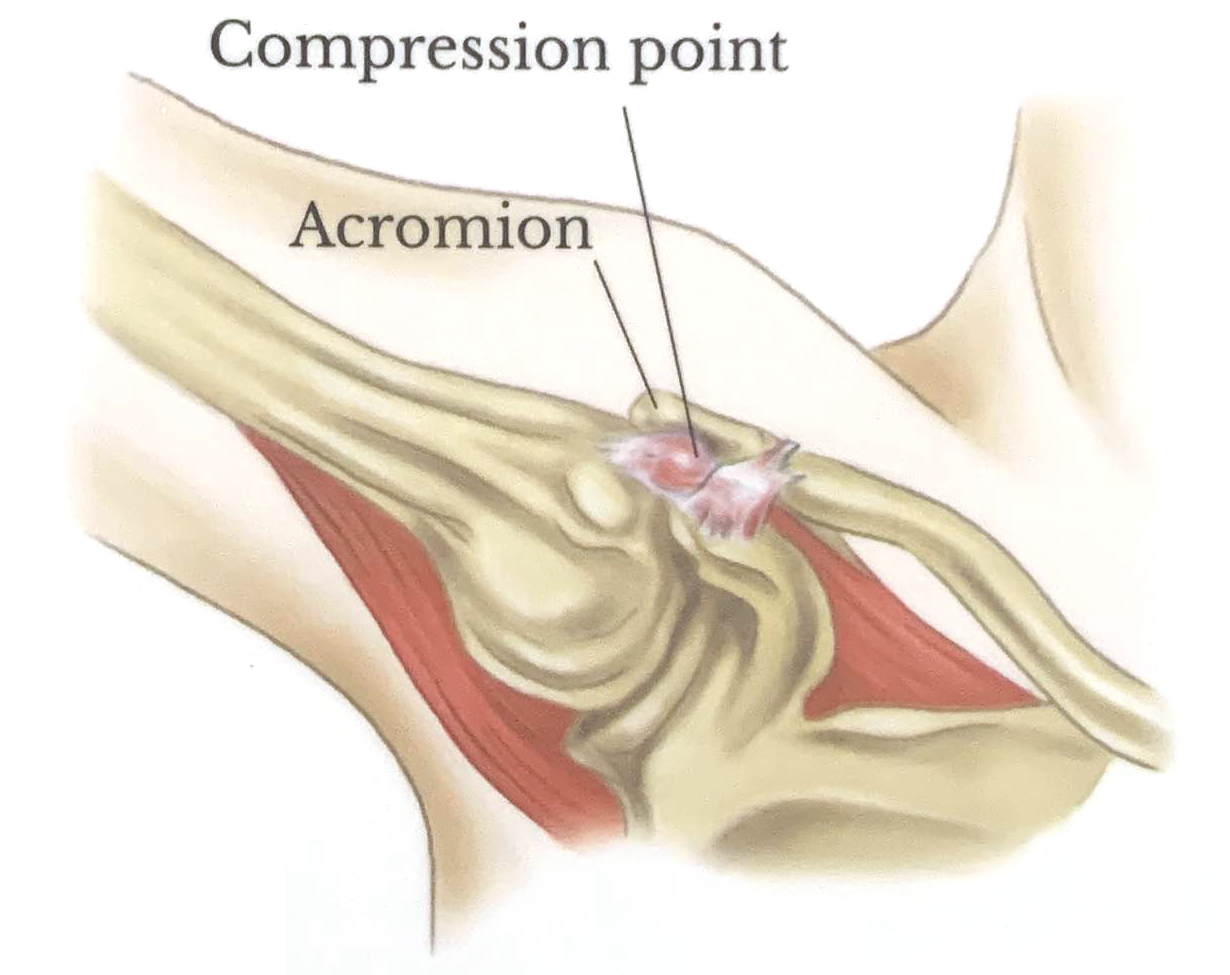
Impinged Joint
Anterior View
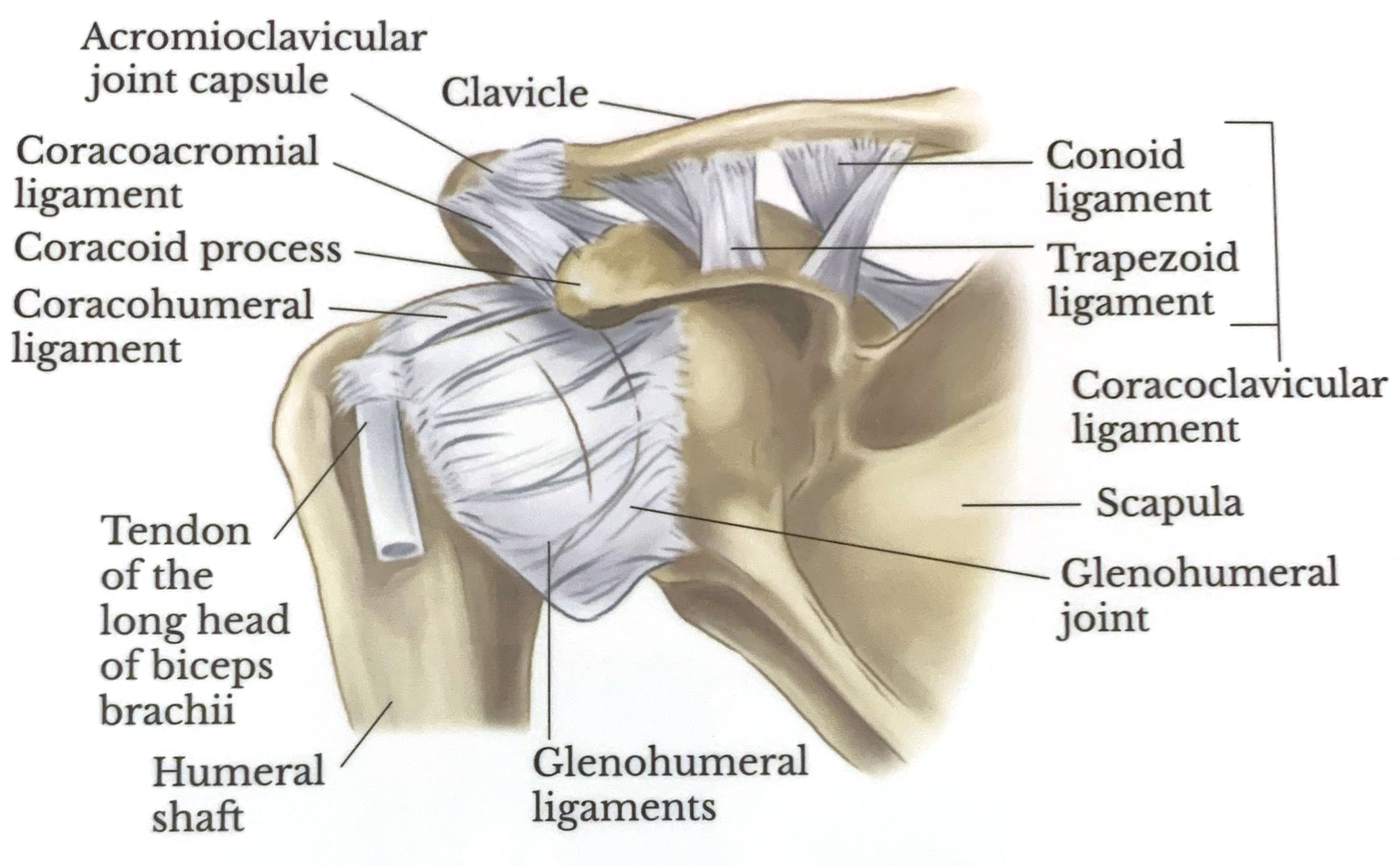
Superior View
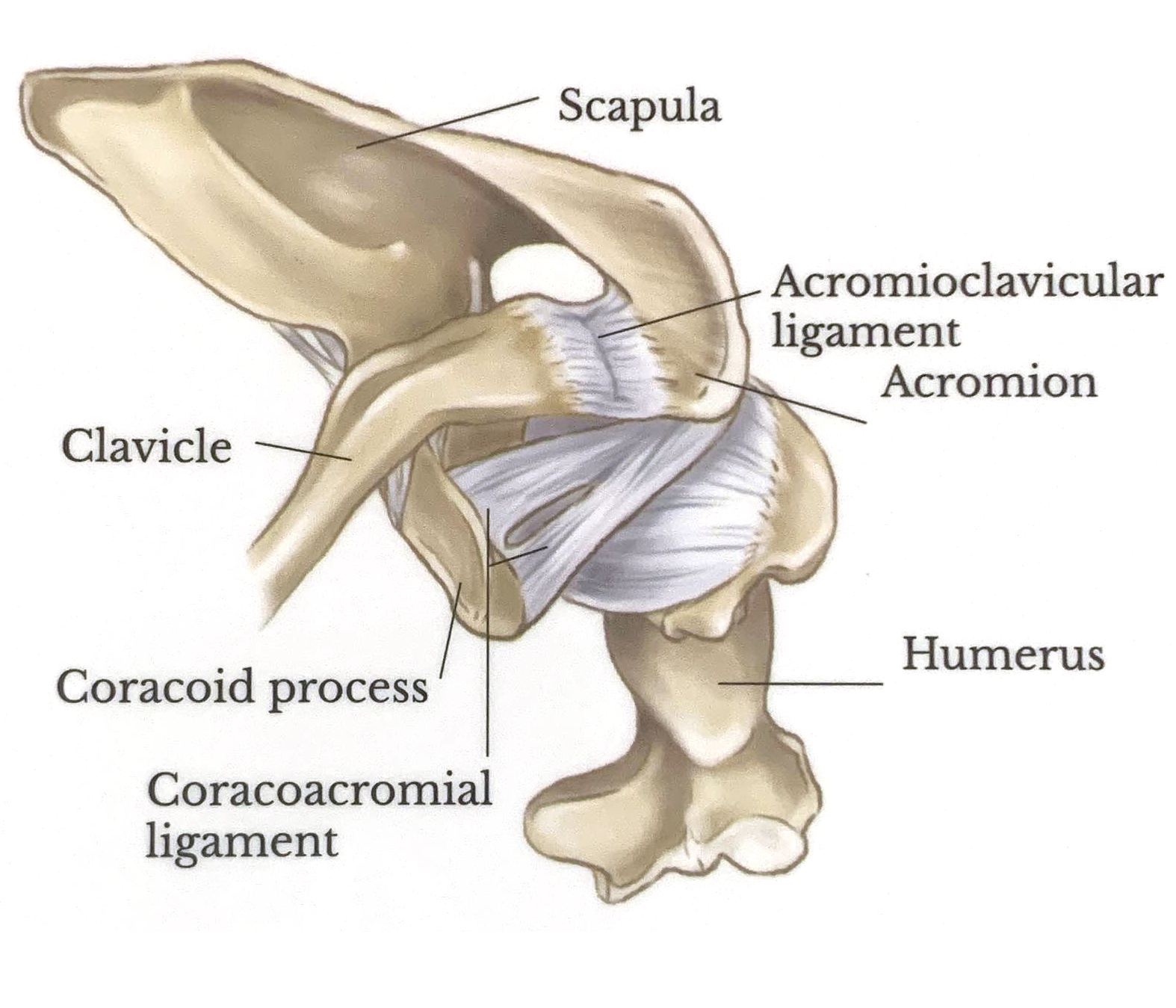
Posterior View
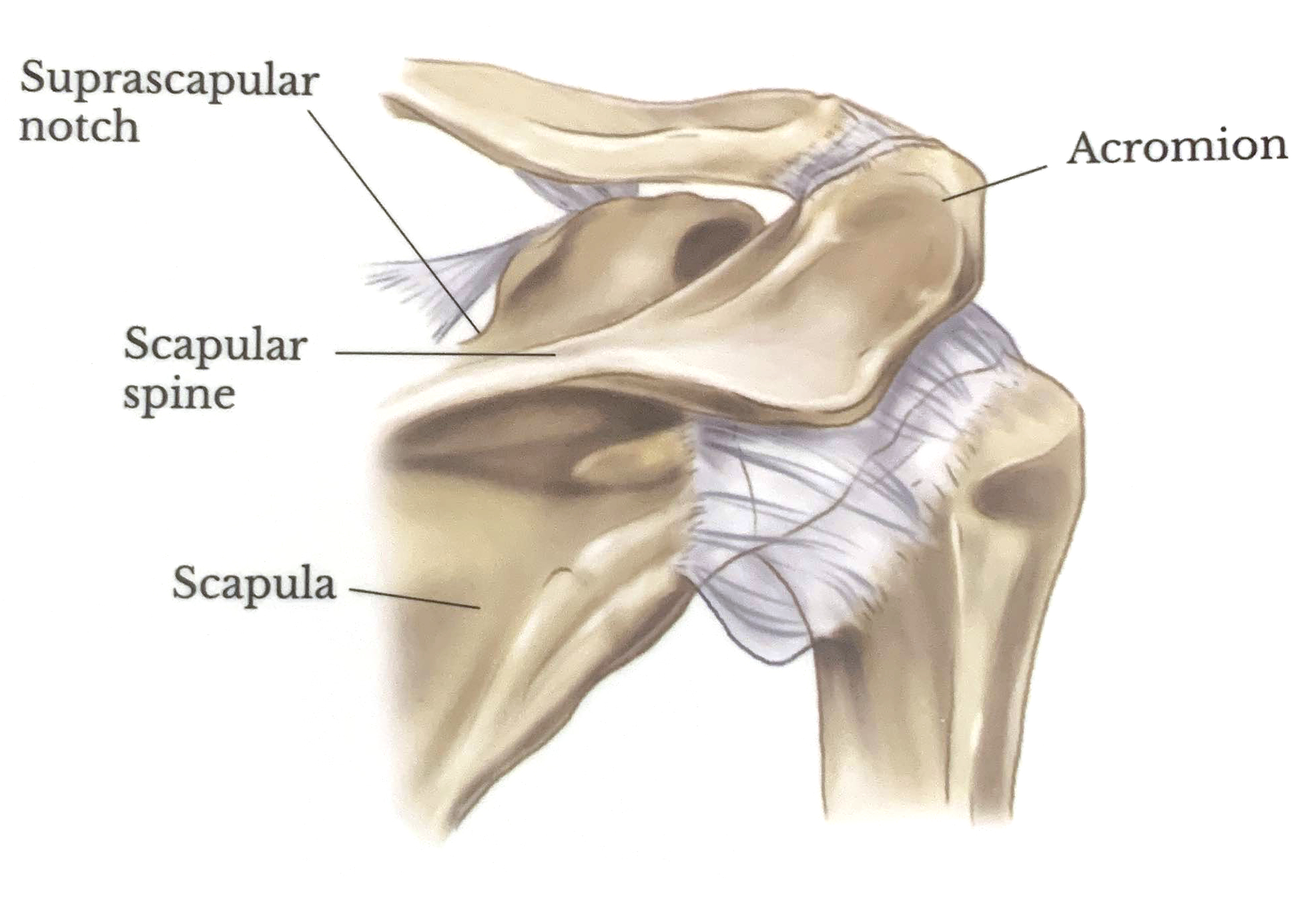
Acromioclavicular Separation
Grades 1-3
The acromioclavicular joint is where the acromion and the clavicle meet. The acromioclavicular, coracoacromial and coracoclavicular ligaments (trapezoid and conoid) stabilize the joint. Injury to these stabilizers causes acromioclavicularseparation - the severity of the injury determines the grade.
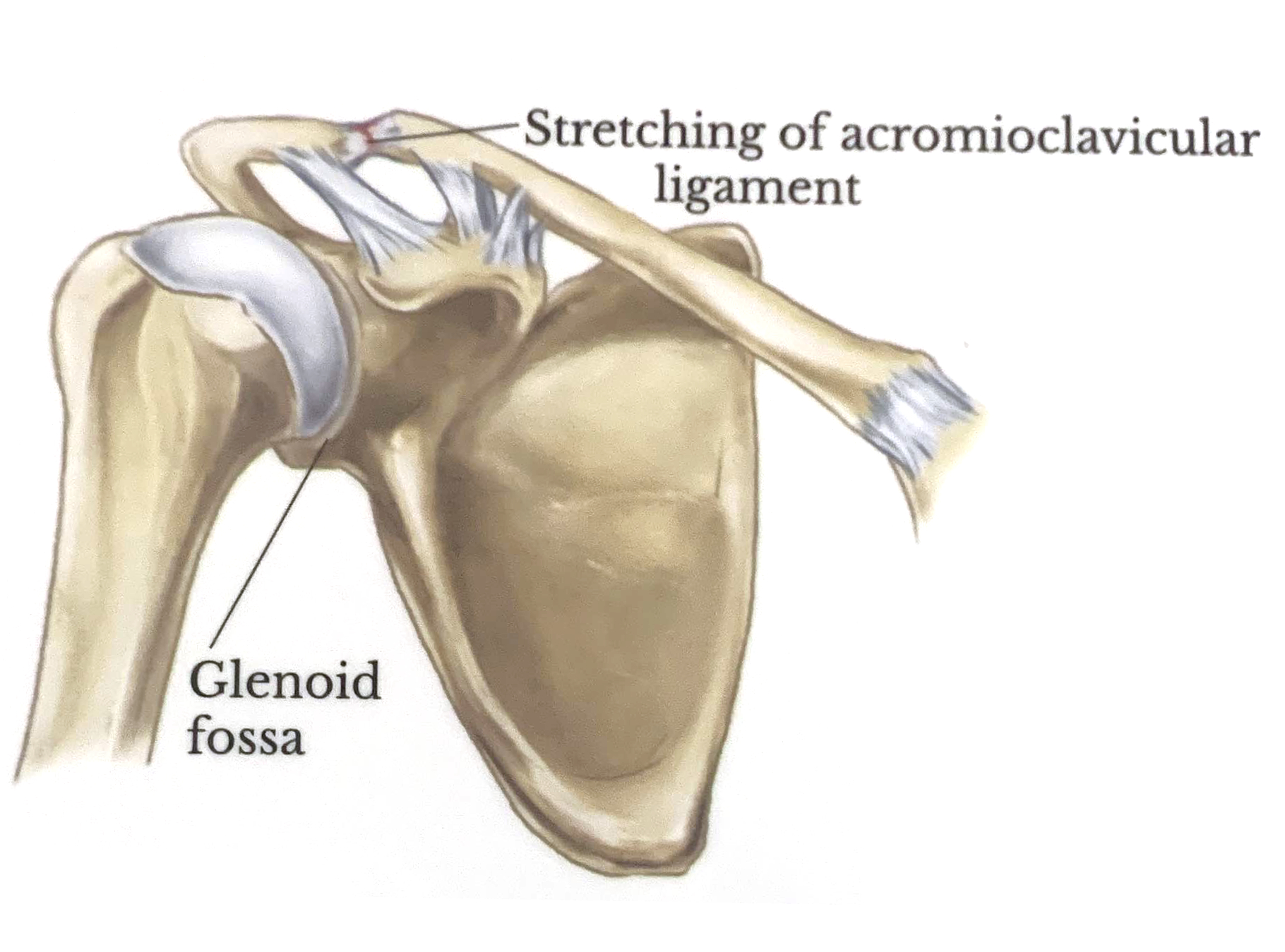
Grade 1
Stretching or partial tear of the acromioclavicular ligament
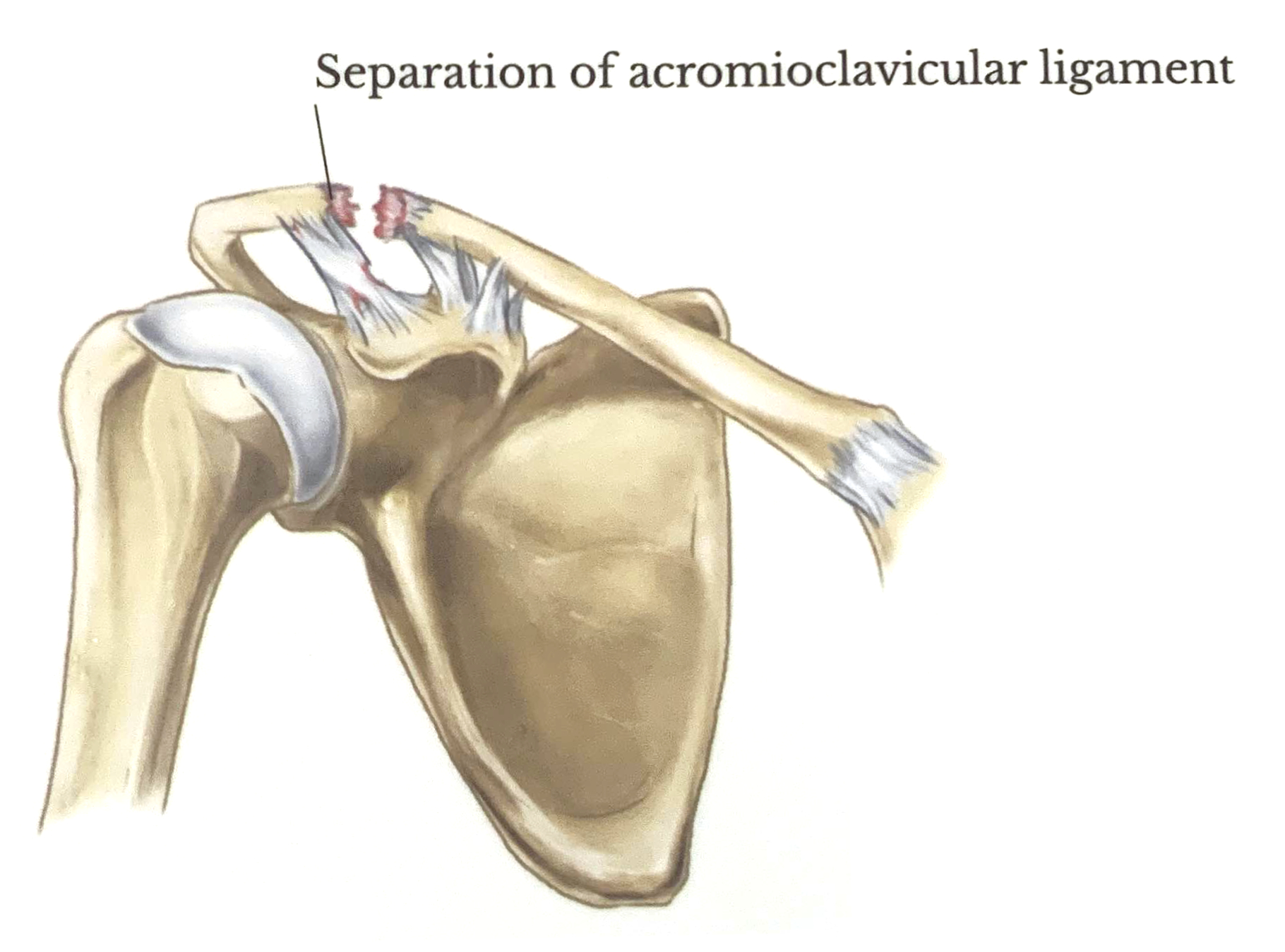
Grade 2
Complete tear of the acromioclavicular ligament
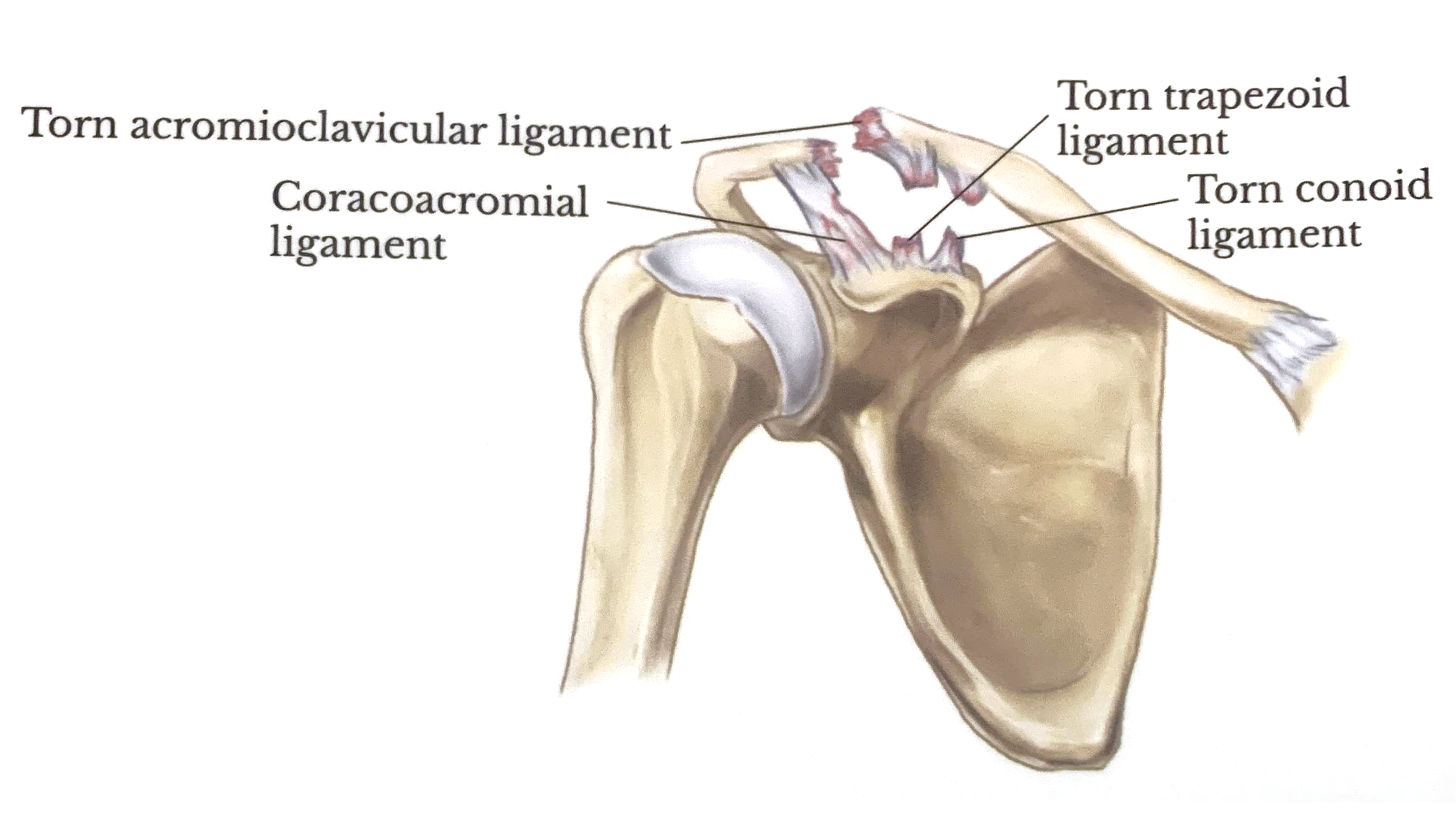
Grade 3
Complete separation of the joint: tears of the acromioclavicular ligament, the coracoclavicular ligaments and the capsule surrounding the joint
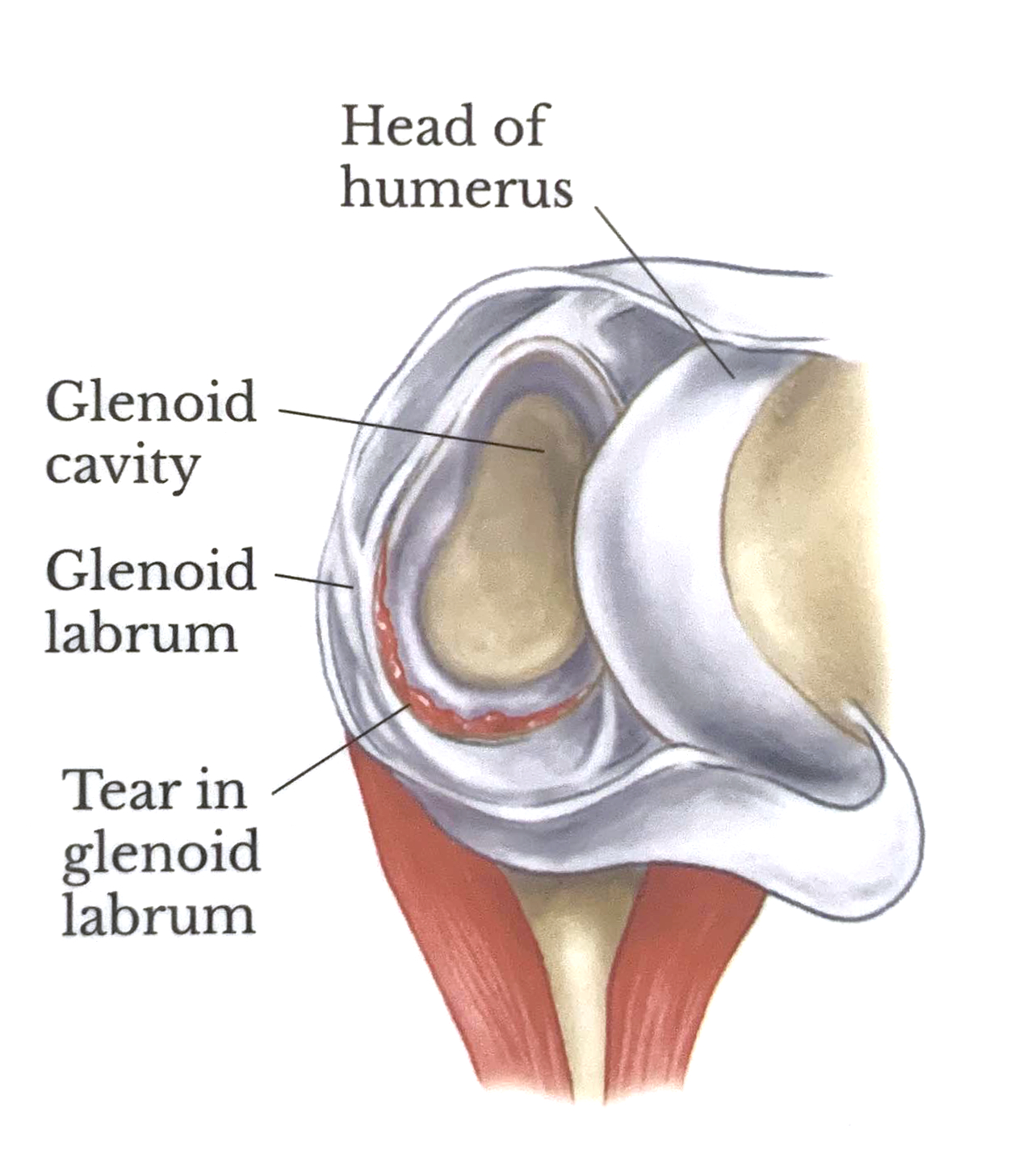
Bankart Lesion
Bankart lesions occur as a result of anterior shoulder dislocations. The anterior inferior glenoid labrum becomes injured. Bankart lesions increase shoulder instability and if left unrepaired make the shoulder more prone to dislocation. Bankart lesions are often seen in combination with Hill-Sachs lesions.
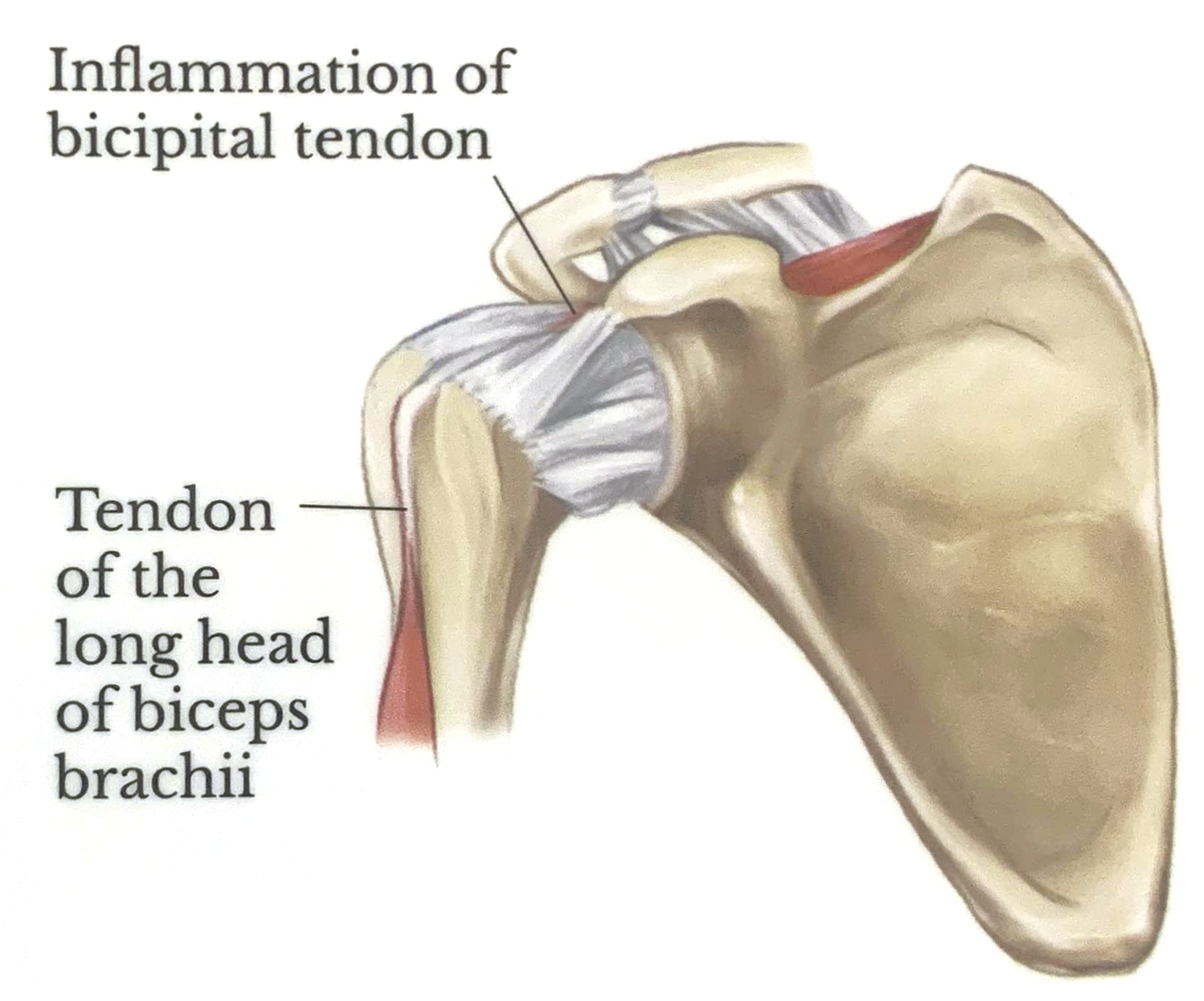
Bicipital Tendinitis
Bicipital tendinitis occurs when excessive tension, pinching, or shearing of the long head of the biceps brachii tendon causes inflammation, leading to swelling and pain.
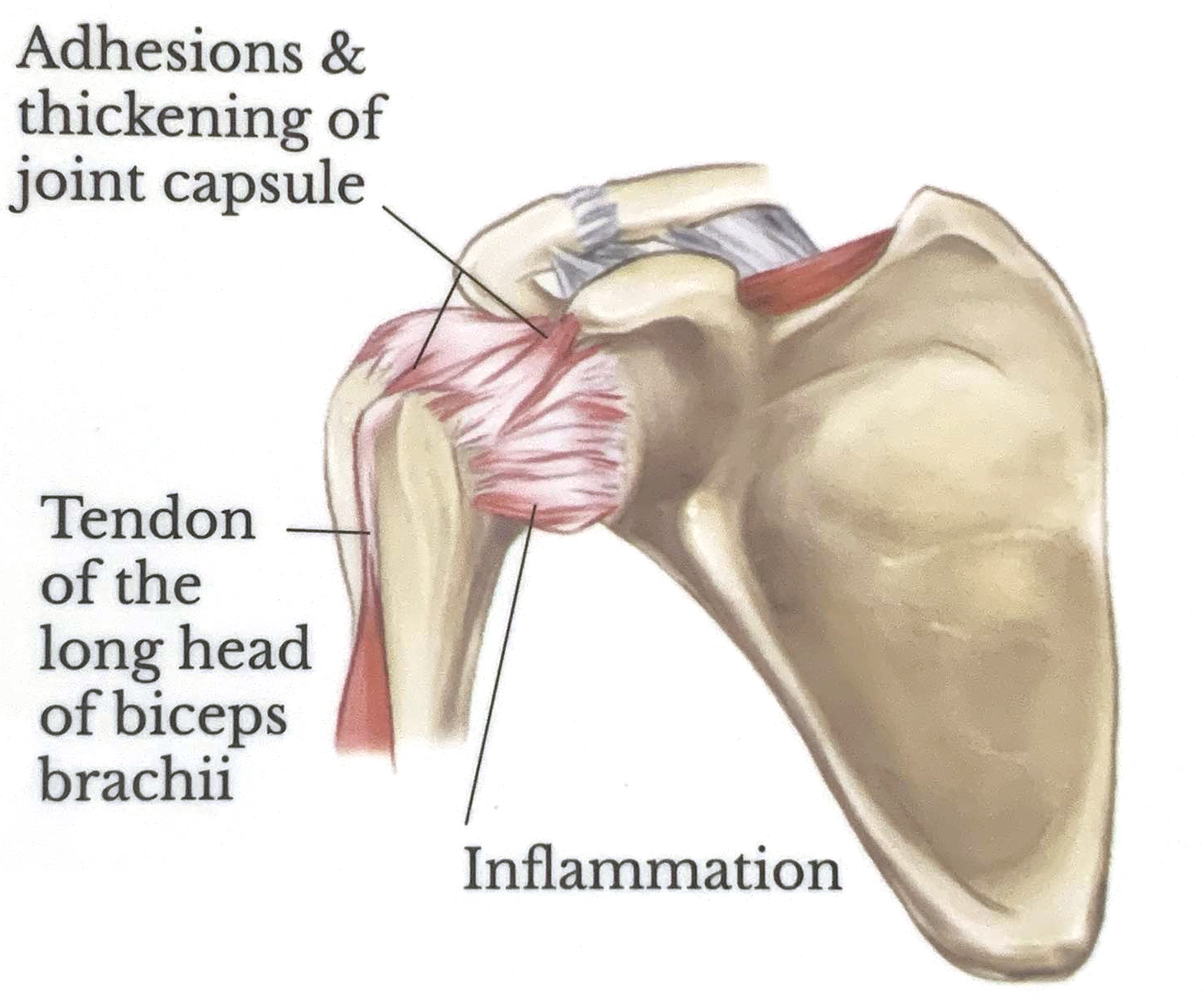
Frozen Shoulder Syndrome
Frozen shoulder syndrom develops gradually and causes joint pain and stiffness. The shoulder capsule becomes thick and tight with scar tissue, limiting movement of the joint.
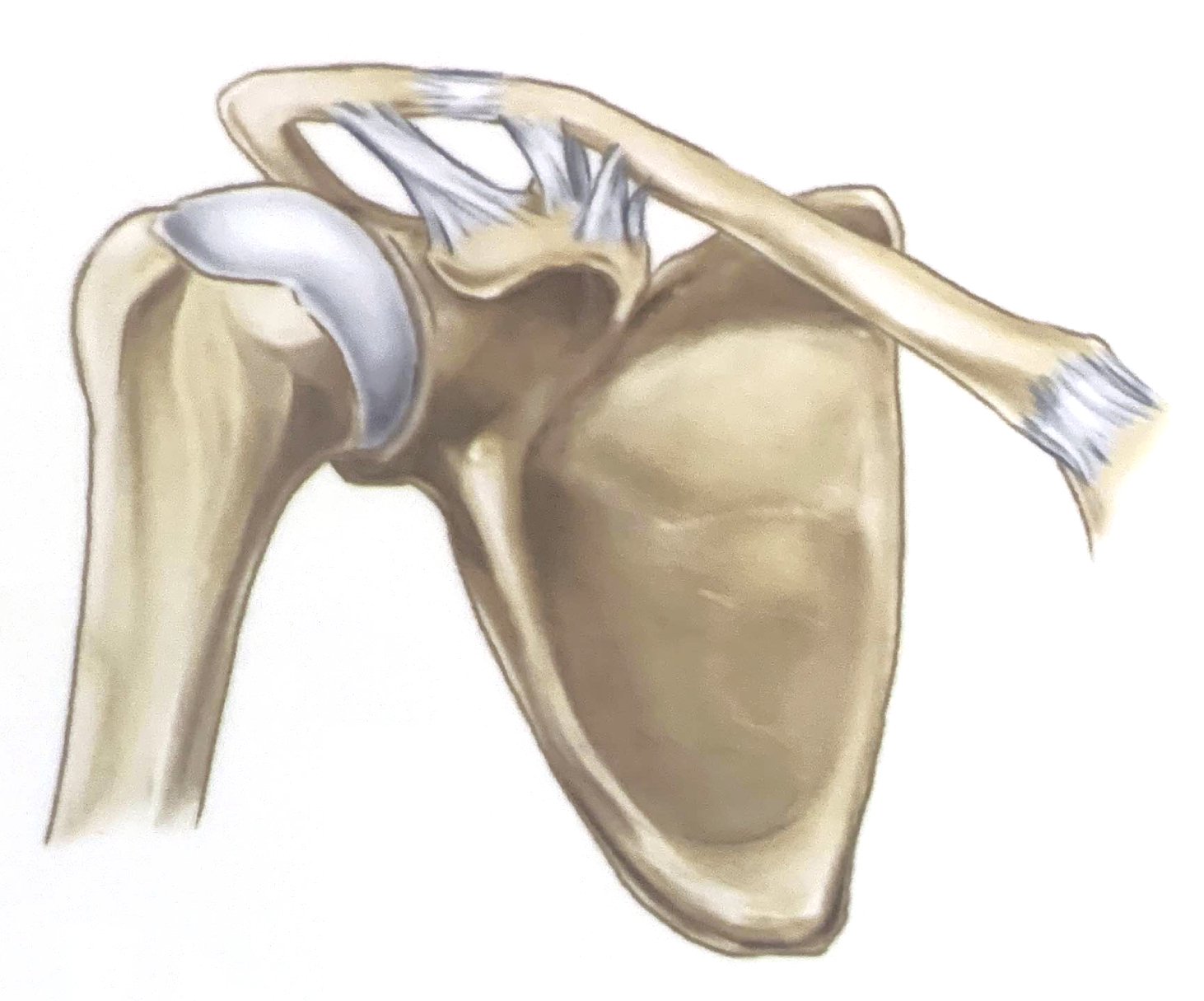
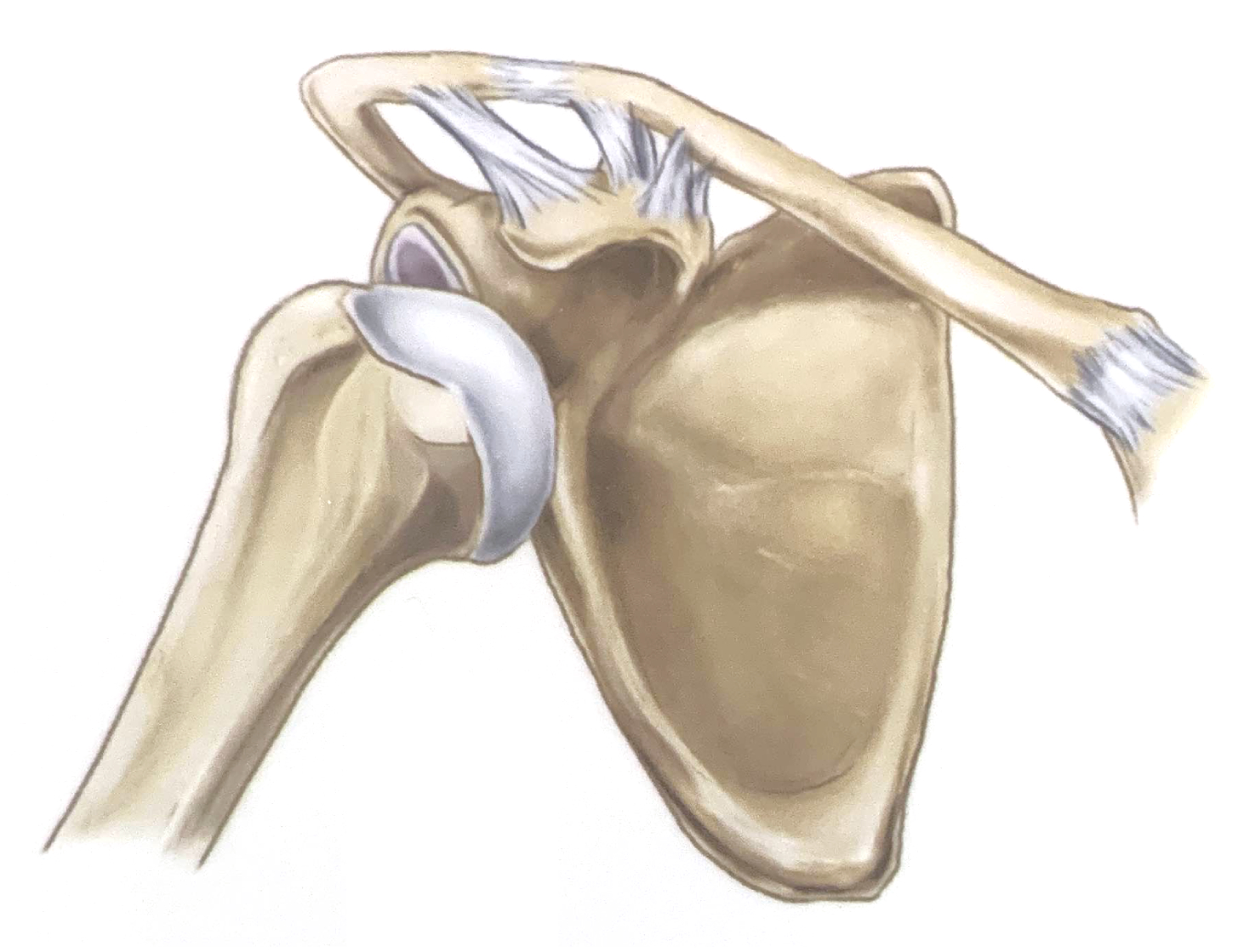
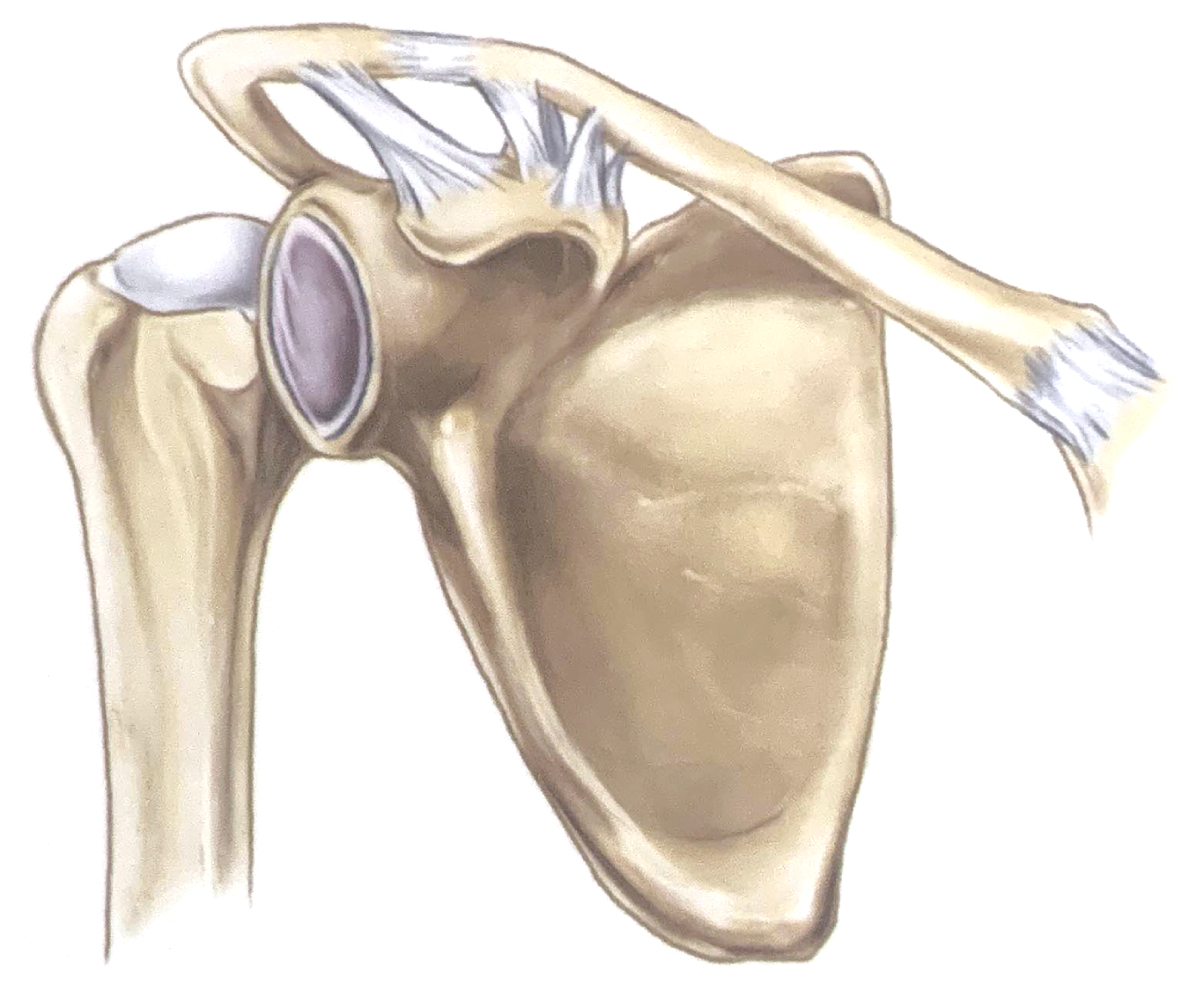
Dislocation of Humerus
There are three types of shoulder dislocations: anterior, posterior, and inferior (not pictured). Anterior dislocations are by far the most common. This is because there is less anterior support to the humeral head.
Normal Position
Anterior Position
Posterior Position
Hill-Sachs Lesion
A Hill-Sachs lesion is an impaction fracture of the posterolateral head of the humerus resulting from recurrent anterior shoulder dislocation.
Hill-Sachs lesions occur with chronic anterior shoulder instability and progress through three grades if left without treatement. Hill-Sachs lesions and Bankart lesions are often seen in combination.
Normal
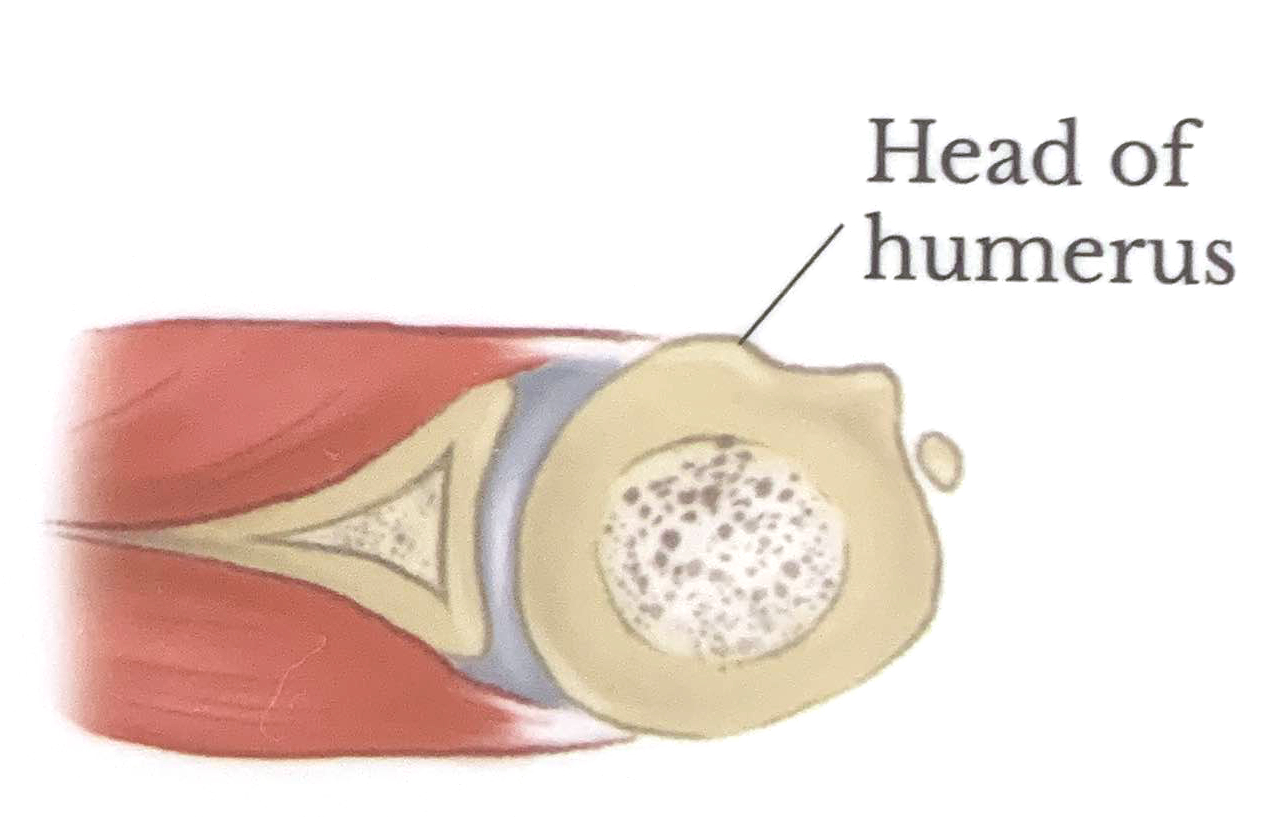
Grade 1
There is a defect in the articular surface down to, but not including, the bone under the cartilage.
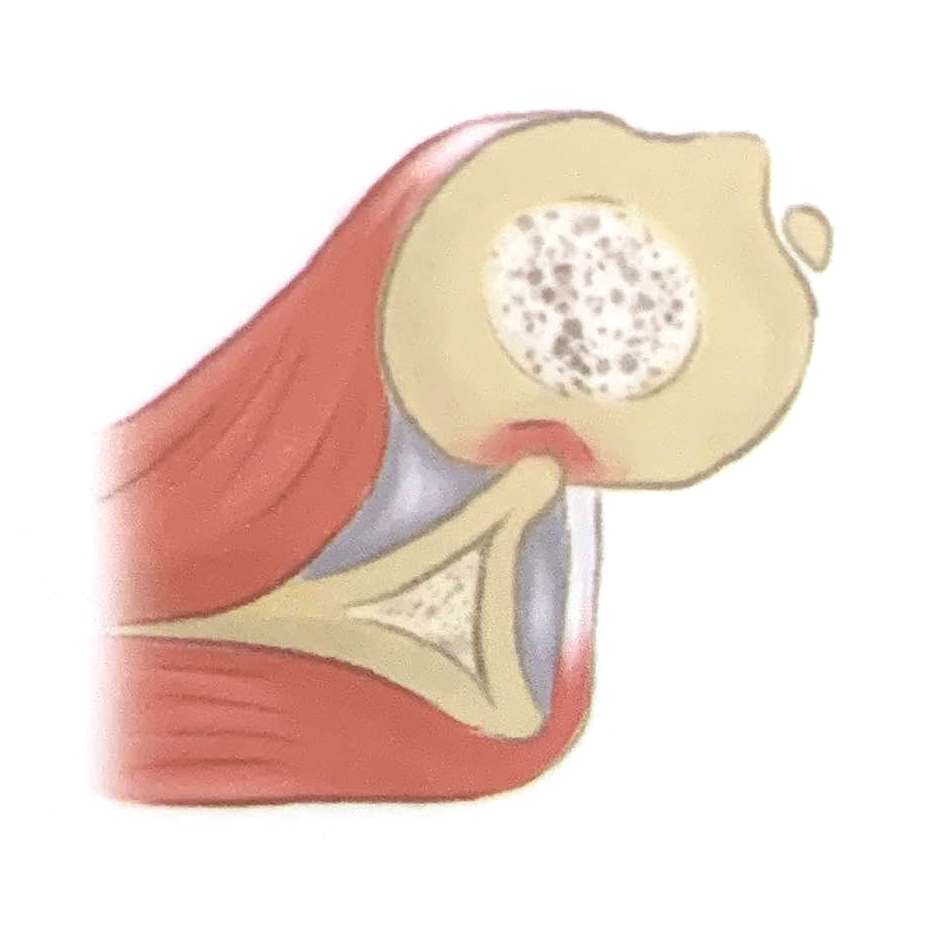
Grade 2
The lesion includes the bone under the cartilage.
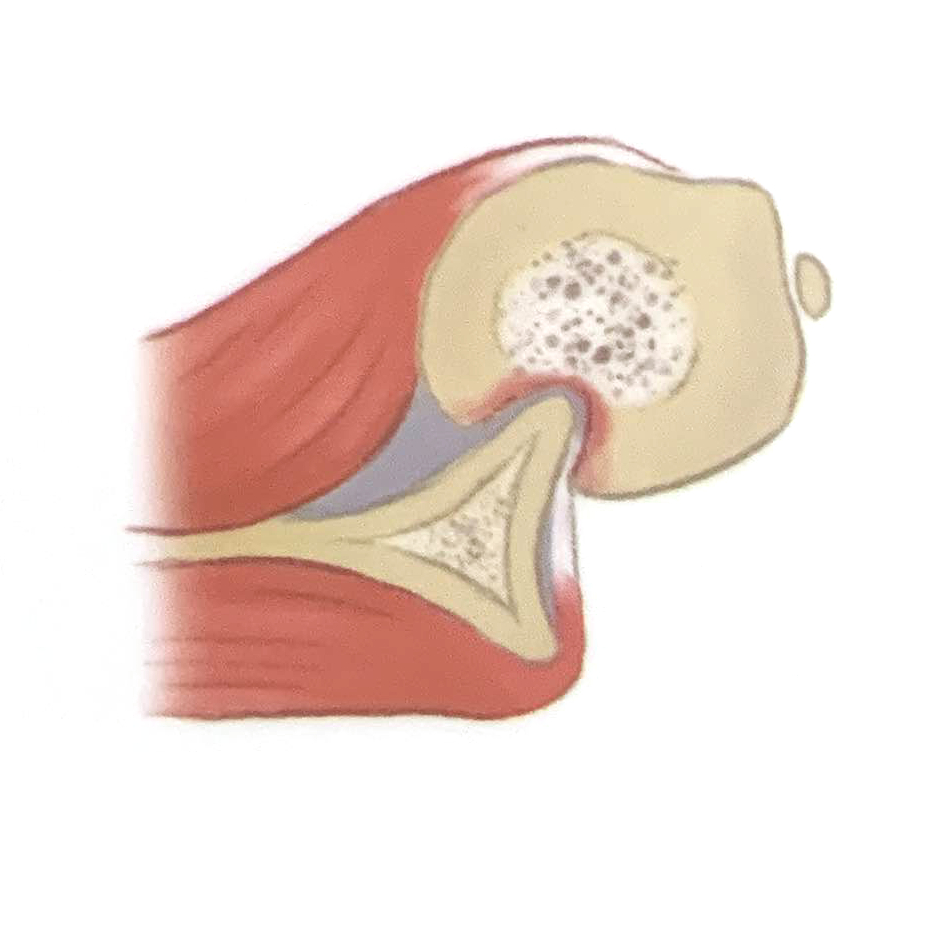
Grade 3
The lesion creates a large defecct in the bone.