Understanding Low Back Pain
Low back pain is a common ailment that affects most people at least once in their lives.
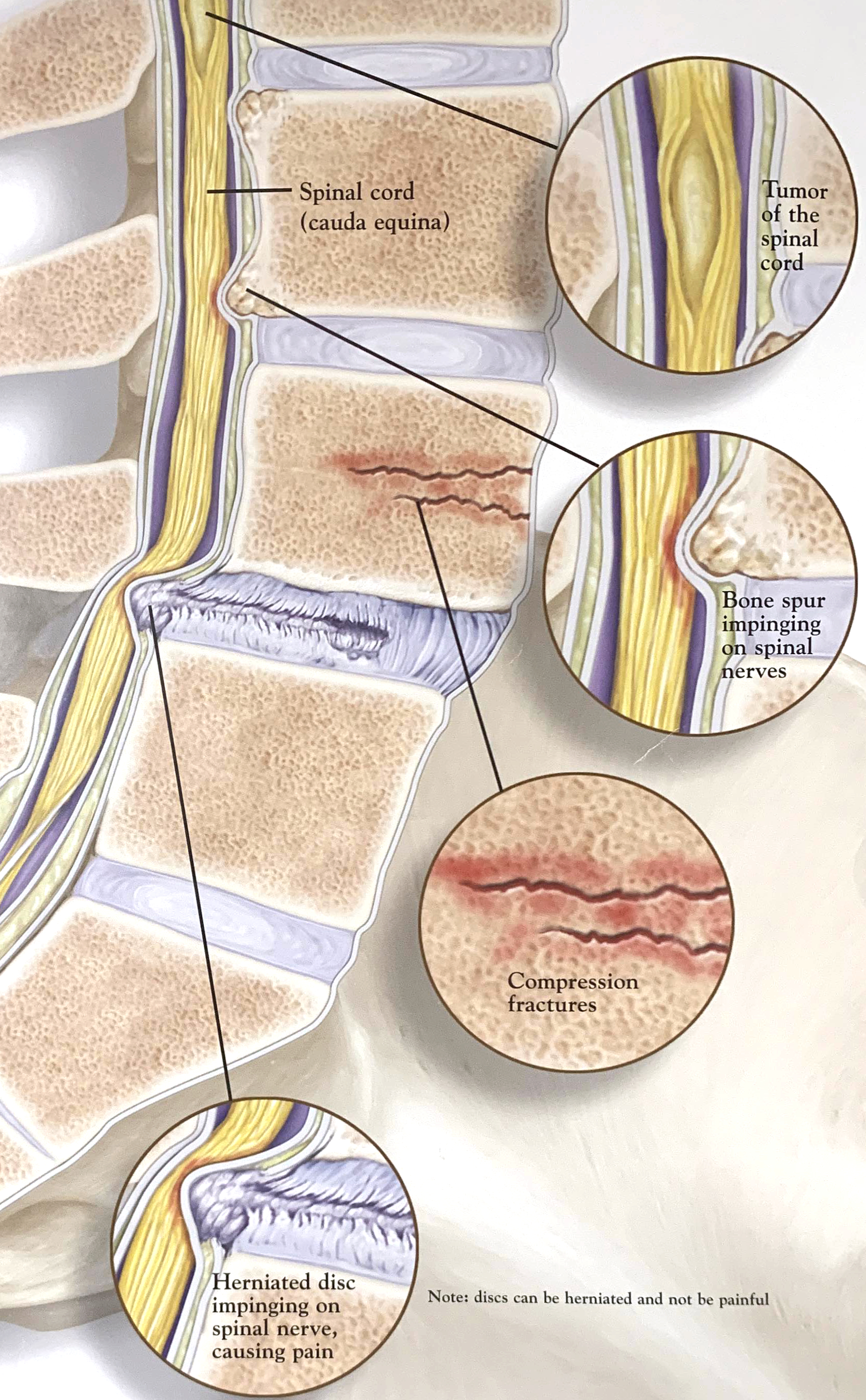
The spine is designed to hold the body upright and serve as its primary support. The low back, which includes the lumbar curvature of the spine, is made up of bones, muscles, nerves, ligaments, tendons and intervertebral discs.
This part of the anatomy has so many complex moving parts, it's no wonder that it requires special care. The best ways to prevent back pain and maintain a healthy back are by keeping muscles strong and flexible, practicing proper lifting techniques and maintaining a healthy body weight.
Types of Low Back Pain
Back pain is classified as acute or chronic. Acute back pain is usually the result of an injury or a sudden jolt and can last from a few days to a few weeks; it is generally resolved within 6-12 weeks. Back pain becomes chronic when it persists for 3-6 months beyond the expected healing time. About 15% of low back pain cases progress from acute to chronic.
There are 3 main types of back pain.
- Non-specific low back pain is not associated with a single known cause and accounts for about 85% if back pain cases. The pain is commonly due to sports injuries and sudden strenuous physical acticities; for example, gardening or home improvement acticities on the weekend after being sedentary during the week.
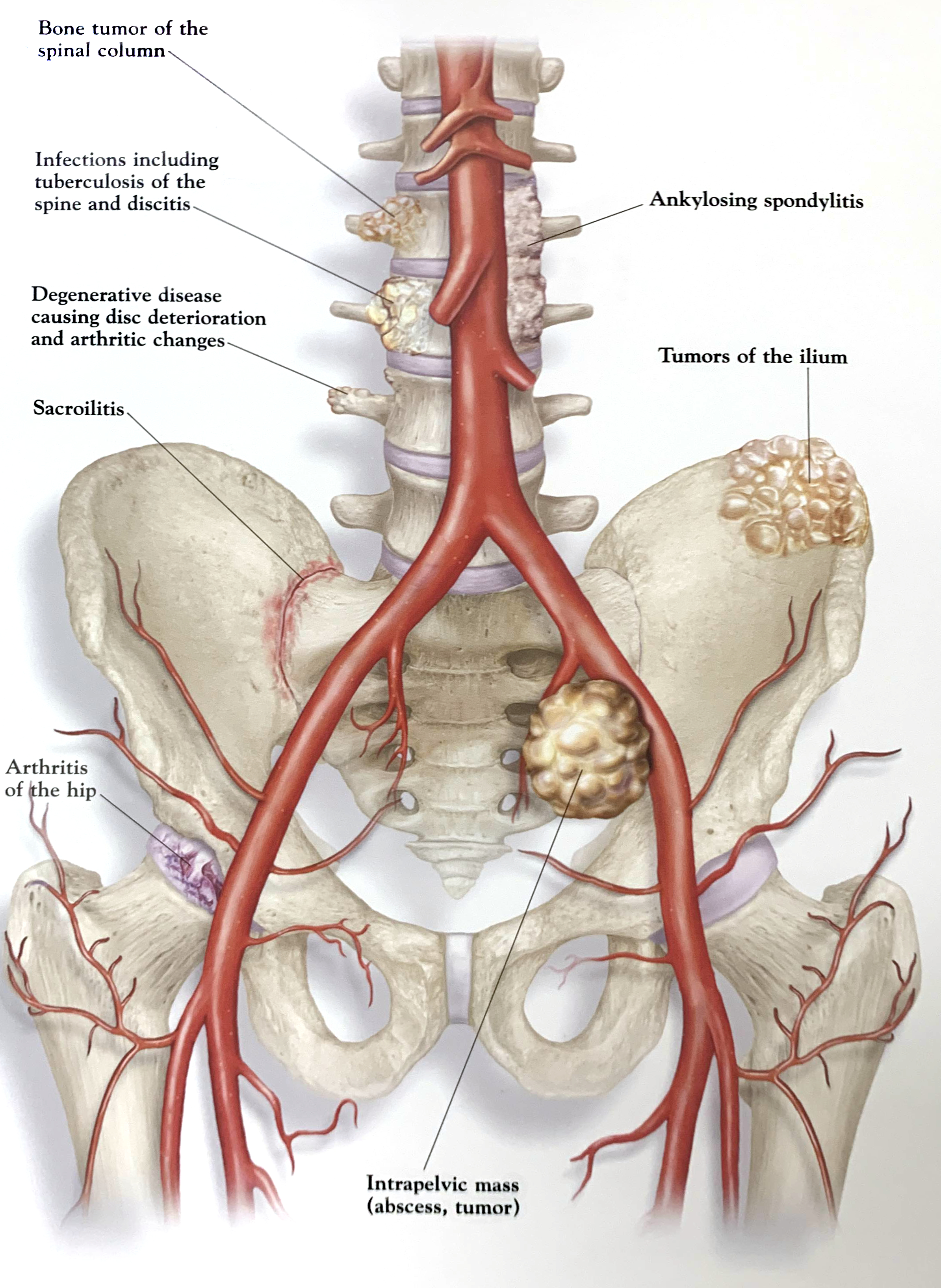
- Back pain caused by various spinal conditions such as sciatica, bulging disc (also called protruding, herniated or ruptured disc), spinal stenosis, arthritis, fibromyalgia, skeletal irregularities and osteoporosis.
- Back pain resulting from a specific trauma; for example, a car accident or cancer.
Causes and Risk Factors
- Age - As people age, bone strength lessens, as do muscle elasticity and tone. The discs in between the vertebrae lose fluid and flexibility which decrease their ability to cushion spinal compression.
- Physically strenious work - Back sprains, strains, spasms, or disc ruptures can be caused by lifting items that are too heavy or by using improper lifting techniques.
- Overstretching
- Poor physical condition - Due to factors such as sedentary life style or unhealthy amounts of exercise (either too little or too much).
- Obesity
- Inappropriate posture
- Poor sleeping position
- Weight gain during pregnancy
- Smoking
- Stress
- Anxiety and/or depression
- Build up of scar tissue from repeat injuries
Other contributing factors related to non-specific back pain include:
Signs and Symptoms
Common symptoms of low back pain include:
- Muscle ache
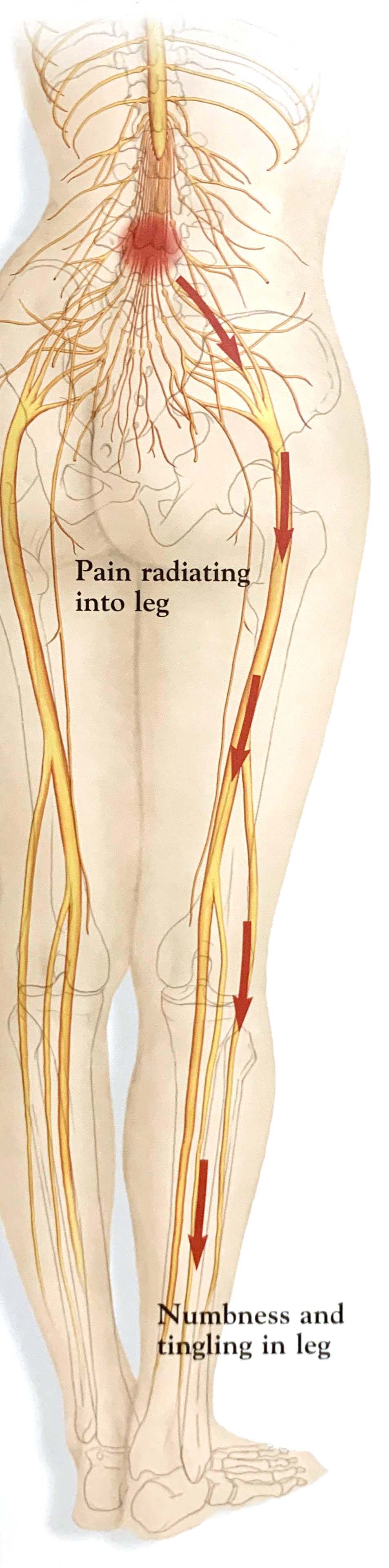
- Shooting or stabbing pain
- Limited flexibility or range of motion
- Inability to stand straight
When ongoing pain is not relieved, chronic pain sufferes may experience:
- Poor sleep quality and lack of concentration
- Inability to perform tasks well at home or work
- Irritability
- Depression
Back pain can indicate a serious condition and can be accompanied by other symptoms such as unintentional weight loss, pain that worsens at night and does not resolve with rest, bladder or bowel incontinence, and weakness in the hands and/or feet. It is important for patients to tell their health care professional about all occuring symptoms.
Treatment and Management
The goal of treatment for low back pain is to reduce pain and restore function, strength, and prevent injury reoccurrence. A combination of treatments may be recommended by your health care professional. In a few serious cases, surgery may be performed to relieve low back pain.
Some common treatments include:
- Ice and heat
- Physical activity; staying in bed can make back pain worse and weaken muscles
- Medications
- - Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS) or acetaminophen
- - Opioids (to help manage pain)
- - Muscle relaxants
- - Medications for sleep and depression
Alternative approaches include:
- Physical therapy
- Spinal manipulation/chiropractic care
- Acupuncture
- Massage therapy
- Biofeedback
- Yoga and relaxation techniques
- Cognitive behavioral therapy
Prevention
Maintaining a healthy back is very important in preventing low back pain. Some techniques include:
Focus on physical and mental well being:
- Exercise regularly with low-impact aerobic activities such as walking and swimming
- Strengthen abdominal and back muscles with core-conditioning exercises
- Practice yoga for strength and flexibility, and stretch well after exercising
- Eat a proper diet
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Quit smoking
- Manage stress levels
Exercise proper body mechanics:
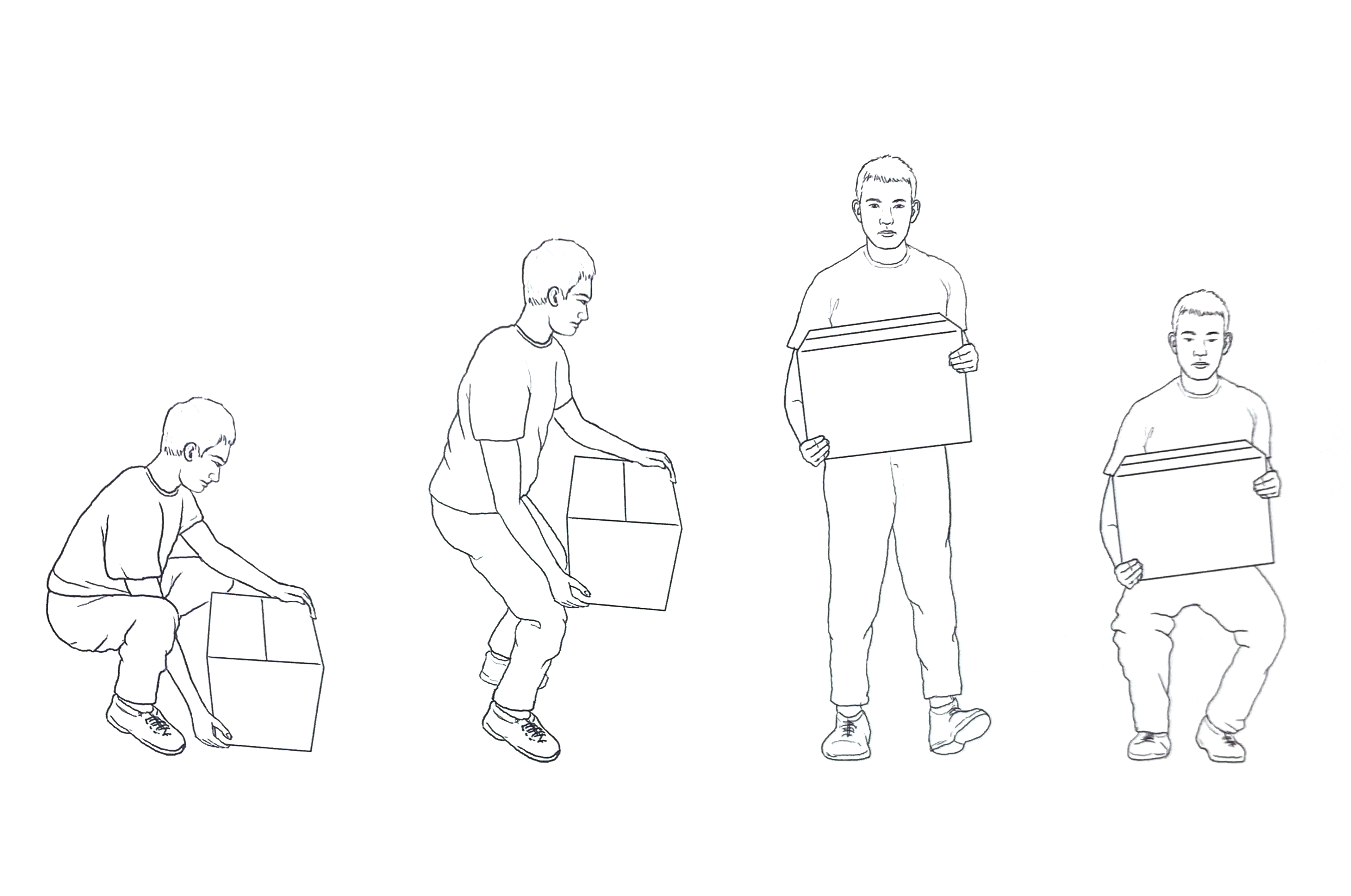
- Practice proper lifting techniques - lift with your knees, keeping your back straight and stomach muscles contracted. Do not lift anything excessively heavy.
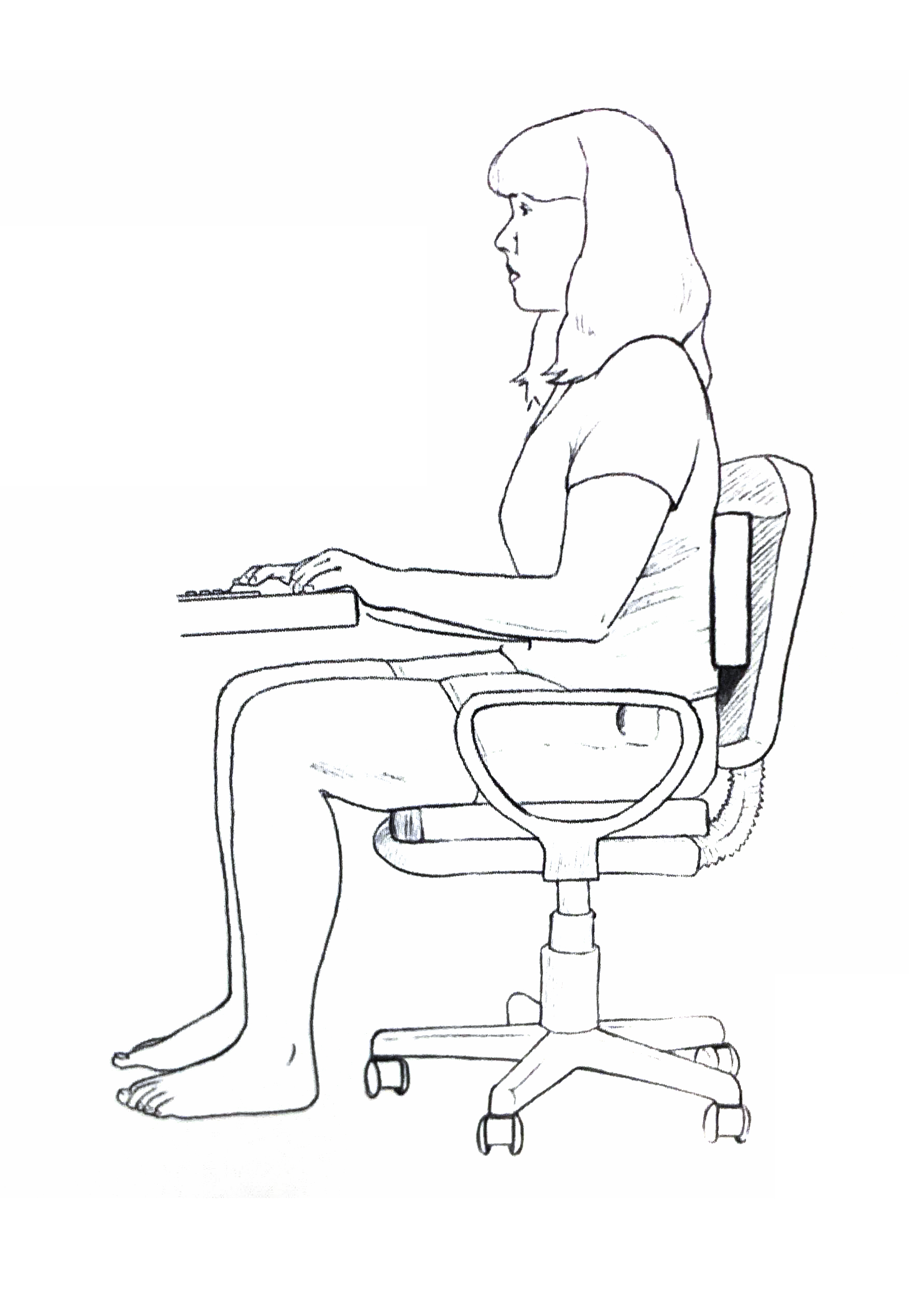
- Utilize ergonomically-designed products, as well as work and living spaces
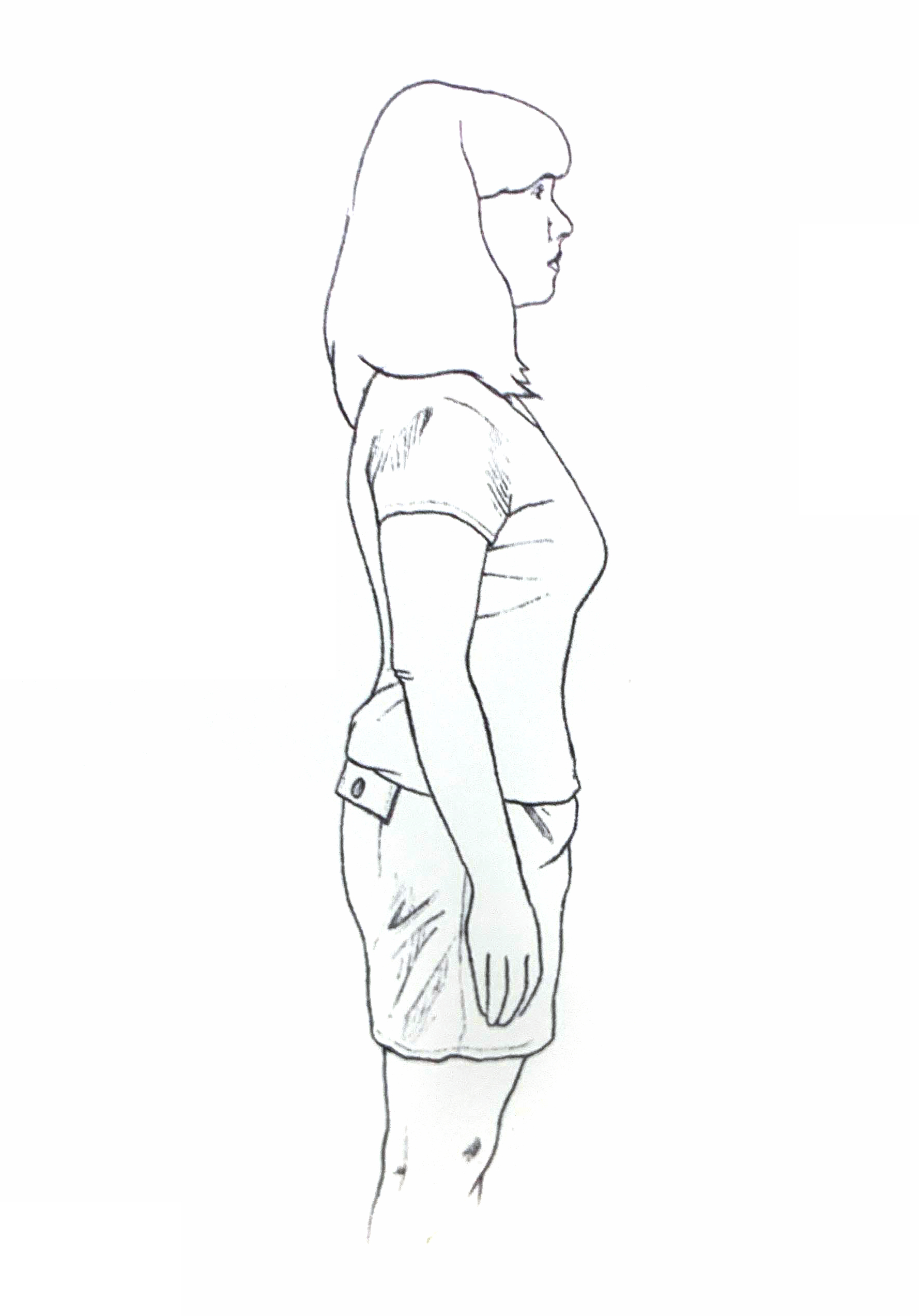
- Maintain proper posture when sitting or standing
- Wear comfortable low-heeled shoes
- Sleep on a firm surface and on your side to reduce curving of the spine
Correct Postures and Techniques to Avoid Low Back Pain
Standing
Sitting at a desk or computer
Lifting techniques
Anterior View, Lower Spine and Pelvic Region
Pain Radiating From Injury
Sagittal View of Lower Spine